Marschall S. Runge, MD, PhD
- Charles Addison and Elizabeth Ann Sanders Distinguished
- Professor of Medicine
- Professor and Chair, Department of Medicine
- Division of Cardiology
- University of North Carolina School of Medicine
- Chapel Hill, North Carolina
Disulfiram dosages: 500 mg, 250 mg
Disulfiram packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase 500 mg disulfiram with amex
Discontinuations from studies due to adverse events Adverse events that are intolerable lead to discontinuation from studies symptoms 7 weeks pregnancy 250 mg disulfiram with amex, although some may take longer to result in discontinuation symptoms 4 days after conception order disulfiram with a mastercard. Such discontinuations take into account the patient’s evaluation of the degree to which the adverse event is tolerable symptoms bacterial vaginosis purchase disulfiram 500 mg amex. The CATIE trials included these discontinuations as a secondary outcome measure and found statistically significant differences among the drugs. In CATIE Phase 1, discontinuations due to adverse events were highest among patients taking olanzapine (primarily due to weight gain or other metabolic effects, 18%) and lowest among those taking risperidone (10%; P=0. Time to discontinuation for adverse events did not differ among the groups. In Phases 1B, 2T, and 2E, differences were not seen between groups for rate of discontinuations or time to discontinuation due to adverse events (intolerability). Data from discontinuation rates from 64 head-to-head trials were used in a mixed- treatment comparisons analysis (also known as a network meta-analysis; Table 10). This analysis used direct and indirect comparisons based on the head-to-head trials and found that clozapine resulted in discontinuation due to adverse events statistically significantly more often than olanzapine, immediate-release quetiapine, or risperidone. This analysis controlled for between study heterogeneity and dose level within study (low, medium, or high) by using the fixed- Atypical antipsychotic drugs Page 65 of 230 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project effects model. It did not control for within study heterogeneity for those studies where there were more than 2 drug arms. As noted previously, dose comparisons have been an issue in this set of studies, with early studies using doses that are not considered clinically optimal now. For example, early studies of risperidone often used doses well above those used today and clozapine and olanzapine studies used doses below those used today. In stratified sensitivity analysis (studies of greater than 6 months in duration) the findings were no longer statistically significant, although the point estimates were in the same direction was the overall analysis. This is most likely due to the lower number of studies in each stratified analysis. There are fewer data available for the newer drugs, particularly iloperidone, asenapine, and paliperidone long-acting injection. Hence, results for these drugs should be interpreted with caution. Atypical antipsychotic drugs Page 66 of 230 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project a Table 10. Mixed-treatment effects model: Rates of discontinuation due to adverse events Aripiprazole Asenapine Clozapine Iloperidone Olanzapine Quetiapine Paliperidone Risperidone Ziprasidone 0. Atypical antipsychotic drugs Page 67 of 230 Final Report Update 3 Drug Effectiveness Review Project Because the 3 of 4 short-term trials of iloperidone were published in an abbreviated fashion and because the lower-dose studies did not indicate superiority over placebo in efficacy, there was very limited data available to evaluate comparative harms with iloperidone. A pooled analysis of 3 unpublished 6-week studies indicated that the proportion of patients discontinuing due to adverse events was highest in the risperidone group (6. Similar results were found in a study including 94 ziprasidone: iloperidone (5%, 24 mg daily), ziprasidone (8%, 160 mg daily), and placebo (8%), and in a pooled analysis of 3 longer-term trials (3. Extrapyramidal symptoms 60 In CATIE Phase 1, differences were not found between olanzapine, immediate-release quetiapine, risperidone, or ziprasidone in the incidence of extrapyramidal symptoms identified as an adverse event, or akathisia or movement disorders based on rating scales. Similarly, 77 64 differences were not found between drugs in the subsequent CATIE Phase 1B, Phase 2E, or 78 Phase 2T, or in another trial with multiple drugs (aripiprazole, olanzapine, immediate-release 62 quetiapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone). In a more detailed analysis of only treatment- emergent extrapyramidal symptoms among patients in CATIE, differences in incidence or severity between the atypical antipsychotic drugs were not found based on rating scales for 304 parkinsonism, dystonia, akathisia, or tardive dyskinesia. The use of antiparkinsonism medications was greater with risperidone and lower with immediate-release quetiapine (P=0. In a 52-week trial of olanzapine, immediate-release quetiapine, and risperidone in patients with early psychosis (median duration of illness 6. This study did find statistically significantly more patients taking olanzapine requiring anticholinergic medication for extrapyramidal symptoms compared with immediate- release quetiapine (4% compared with 11%; P=0. Data or analysis for comparison on immediate-release quetiapine and risperidone were not reported. A study of patients with acute schizophrenia, conducted in the inpatient setting over 3 weeks, found no statistically significant difference in symptom scores among aripiprazole, haloperidol, olanzapine, immediate-release 62 quetiapine, risperidone, or ziprasidone. This study reported that 30% of patients taking risperidone and 10% taking immediate-release quetiapine or ziprasidone required anticholinergic medication for extrapyramidal symptoms, while no patient taking aripiprazole or olanzapine did. In head-to-head trials comparing only 2 drugs, differences were not found between 55, 76, 83 olanzapine and immediate-release quetiapine in 3 studies, clozapine and olanzapine in 5 28, 68, 82, 104, 305 38, 65, 99 studies, or olanzapine and aripiprazole in 2 studies.
Best buy disulfiram
Rizatriptan showed consistently higher 2-hour response rates than placebo during headache 1 (77% [320/246] compared with 37% [30/82]; P<0 medicine for uti buy discount disulfiram 500 mg on line. However treatment non hodgkins lymphoma quality 500 mg disulfiram, it is unclear whether differences between rizatriptan and placebo groups in the number of patients excluded from the analyses of headache 2 (9% compared with 11%) medications high blood pressure buy cheap disulfiram online, headache 3 (19% compared with 8%), and headache 4 (20% compared with 30%) may have resulted in groups compared after headache 1 being dissimilar in important patient characteristics that could have biased the analyses. The efficacy of rizatriptan 10 mg administered early in a migraine, while pain is mild, has been demonstrated in 2 identically designed, good-quality placebo- 63 controlled trials named Rizatriptan TAME1 (Treat A Migraine Early) and TAME2. Findings from TAME1 and TAME2 were both reported in a single publication. Eligibility criteria required a history of migraines that typically started out mild. The study plan was for patients to treat their migraines while still mild in severity and present for less than 1 hour, but not spontaneously resolving. In both trials, rizatriptan was superior to placebo in rates of 2-hour pain-free and 24- hour sustained pain-free. Rates of 2-hour pain-free for rizatriptan compared with placebo in TAME1 were 57% and 31%, respectively, and in TAME2 were 59% and 31%, respectively (P not reported for pairwise comparisons). Rates of 24-hour sustained pain-free for rizatriptan compared with placebo in TAME1 were 43% and 23%, respectively, and in TAME2 were 48% and 25%, respectively (P not reported for pairwise comparisons). Based on our independent random-effects meta-analysis (Appendix D), these findings resulted in a pooled relative risk of 1. Triptans Page 29 of 80 Final Report Update 4 Drug Effectiveness Review Project For 24-hour sustained pain-free rates, we calculated a pooled relative risk of 3. Rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablets Direct comparisons Rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg compared with the conventional tablet form of sumatriptan 100 mg. We found no head-to-head trials that compared rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg to sumatriptan 100 mg; that evaluated quality-of-life, workplace, or consistency outcomes; or that evaluated early treatment of mild migraine. Two open, fair-quality trials demonstrated rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg to be superior to the conventional tablet form of sumatriptan 50 mg on preference and rates of 2-hour normal function 39, 41 and pain-free. Similar numbers of patients had recurrence of migraine within 24-hours with both rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg and the conventional tablet form of sumatriptan 50 mg. Only 1 of the 2 trials reported 24-hour sustained pain-free outcomes, and the rate was significantly greater for rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg than the conventional tablet form of sumatriptan 50 mg (41% compared with 32. Rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg compared with eletriptan 40 mg. We also found 1 fair-quality, open head-to-head trial primarily designed to evaluate preference for rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg compared with eletriptan 40 mg in 439 adults who 38 had no prior experience with either triptan. Greater numbers of patients expressed a preference for treatment with rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg (61%; 95% CI, 56 to 66) than eletriptan 40 mg (39%; 95% CI, 34 to 44), with the most common reason being “relieved my headache pain faster. Rates of 24-hour sustained pain-free were also similar for rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg (43%) and for eletriptan 40 mg (47%). Placebo-controlled trials: Rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet We did not find any placebo-controlled trials that evaluated rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg for consistency over multiple attacks. We are aware of a placebo-controlled trial of rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg for early treatment of migraine (N=207), for which an in-press article is pending publication in an upcoming issue of Headache. However, it was brought to our attention after our search end date of January 2009 and, consequently, a review of its findings will be postponed until the next update of this review. Although we did not find any published quality-of-life data, the manufacturer provided 61 64 unpublished data for 1 published placebo-controlled trial. This trial involved treatment of 555 adults with moderate to severe pain intensity and prior triptan use was allowed. The Migraine- Specific Quality-of-Life Questionnaire was used to measure quality of life at 24 hours; rizatriptan orally disintegrating tablet 10 mg was superior to placebo (P<0. Triptans Page 30 of 80 Final Report Update 4 Drug Effectiveness Review Project Zolmitriptan: Oral tablet, orally disintegrating tablet, nasal spray Direct comparisons: Oral tablet We included head-to-head trials of oral zolmitriptan 5 mg compared with the conventional tablet 45 44, 46 form of sumatriptan 100 mg and 50 mg. We also identified unpublished data from a trial comparing zolmitriptan 2. The trials involving the conventional tablet form of 12, 65 65 sumatriptan and naratriptan 2. All 3 trials involved treatment of moderate to severe migraines. The trials comparing zolmitriptan 5 mg with the conventional tablet form of 44, sumatriptan 50 mg provided data on consistency of treatment across 6 consecutive headaches.
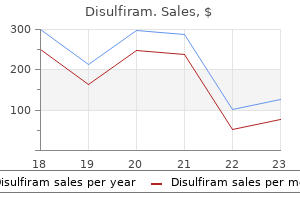
Discount disulfiram 500 mg visa
There are also several novel approaches being pursued in preclinical work or early phase 1 trials medicine cabinet shelves buy online disulfiram. These novel approaches are intriguing symptoms ptsd 500 mg disulfiram buy amex, In a phase 1 clinical trial symptoms pregnancy best order disulfiram, Novo Nordisk demonstrated a glycoPEG- but much remains to be determined as they enter clinical ylated FVIII that increased plasma t1/2 by 1. Further details will be needed to assess the significance FVIIIa serves as a cofactor for FIXa to increase the Vmax and of this finding. It is possible that small molecules might this discussion. One is rhFVIII-hCL, a recombinant FVIII manufac- replace the FVIII function by promoting the assembly of FIXa and tured in a human cell line and currently in phase 3 in adults and FX in a manner that stimulates the rate of FXa generation. Such a children and in clinical trial for previously untreated patients with 55,56 small molecule could be delivered subcutaneously or even orally. The potential advantages are improved t1/2 and this direction, a humanized bispecific mAb to FIXa and FX was possibly a lower rate of inhibitor development in previously derived (hBS23) that displayed a 2-week t1/2 in a cynomolgus untreated patients due to human glycosylation patterns. A phase 1 study in 64 new FVIII product was modified by recombinant technology so that Japanese and Caucasian healthy adults indicated that ACE910 the FVIII is a single chain molecule, scFVIII. It has a higher affinity (hBS23 with additional minor molecular engineering) at doses up to to VWF, which may translate into a longer t1/2, and it is currently in 18,39,57,58 1 mg/kg had medically acceptable safety and tolerability profiles a phase 3 clinical trial. The 2 recently approved the antithrombotic pathways that control coagulation. The tissue 1/2 products were also approved for use in surgery. The phase 3 clinical factor/FVIIa/FXa complex forms small amounts of thrombin to trials for each product include an arm for use in surgery, but all of initiate coagulation. The tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) the results have not yet been reported. Nonetheless, it is reasonable inhibits this complex through its 2 Kunitz domains: Kunitz domain to conclude that the extended t products can be used for surgery 1 interacts with FVIIa and Kunitz domain 2 interacts with FXa. Dosing considerations should target the same monoclonal antibody to the second Kunitz domain neutralizes the peak and trough factor activity levels as for currently used factor inhibitory effect of TFPI on extrinsic pathway activation. One is a nucleic acid ate assays to monitor factor activity after infusion will need to be aptamer that binds tightly and specifically to TFPI and inhibits its function in vitro and in vivo. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)- charide (NASP) BAX 513 demonstrated efficacy in hemophilia dogs. There is some concern that inhibition of TFPI by products currently in phase 3 clinical trials. Further studies planned or under way to provide more detailed guidance for assays in animals and humans will be needed to sort out the therapeutic to monitor the new products as they receive approval for clinical opportunities of these potentially exciting approaches. Targeting antithrombin FVIIa products in clinical trials Another novel approach is represented by the development of FVIIa has been used commonly for nearly 20 years for the treatment ALN-AT3, a synthetic, GalNAc-conjugated RNAi therapeutic de- of patients with inhibitory antibodies and now there are other FVIIa signed to suppress liver production of antithrombin (AT) mRNA 360 American Society of Hematology after subcutaneous injection. Reducing AT levels has the potential there may be increased potential for preventing spontaneous bleed- to reduce the stoichiometric inhibition of thrombin and thus ing, and, perhaps most importantly, to allow individuals with improve hemostasis for patients with hemophilia. Subcutaneous hemophilia B to have a more normal quality of life. In the near administration of ALN-AT3 resulted in dose-dependent and revers- future, there will be other factor products with extended t1/2 for both ible reduction of circulating AT, with a single-dose ED50 of 1 hemophilia A and B, and there may be alternative approaches for mg/kg in multiple species. Future concerns include: (1) how will the costs of these sis in hemophilia A and B mouse models. In a microvessel laser new factor products influence their clinical use? As was the case over the past 25 fibrin at the site of injury, as quantified by intravital microscopy. Extensive toxicology studies of ALN-AT3 have clear answers to guide future hemophilia treatment. Greater than 90% reduction in AT Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author has received research in wild-type animals led to thrombotic events. In contrast, reduction funding from Bayer, Biogen, Octapharma, CSL Behring, NovoNor- by ALN-AT3 to 5% AT levels was well tolerated in hemophilia A disk, Baxter, and REV-Bio. Powell, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Suite 3016, University of California Davis Medical Center, 4501 X Street, Sacramento, CA 95817; e-mail: jspowell@ucdavis. Future concerns of novel molecules A major concern in hemophilia A is the development of neutralizing References antibodies (inhibitors) that prevent further use of therapeutic 1.
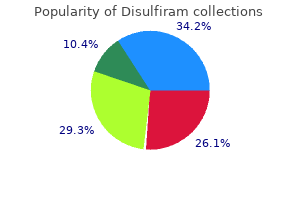
Cheap 500 mg disulfiram visa
Mathematical analysis could establish the necessary conditions to maintain polymorphism for controls of the immune response by trade- offs between high and low expression symptoms joint pain cheap 250 mg disulfiram otc. Such models would clarify the kinds of experiments needed to understand these polymorphisms treatment nerve damage 500 mg disulfiram sale. Effects of regulatory variability on antigenic diversity schedule 9 medications disulfiram 250 mg purchase mastercard. First, different patterns of immune regulation may affect immunodominance (Badovinac et al. Second, immune regulation may affect theintensityandduration of memory. Immuno- logical memory shapes antigenic diversity because a parasite often can- not succeed in hosts previously infected by a similar antigenic profile. Regulatory variability as model for quantitative variability. The widespread genetic variability of quantitative traits forms a classical un- solved puzzle of genetics. To solve this puzzle, one must understand the links between nucleotide variants, the regulatory control of trait de- GENETIC VARIABILITY OF HOSTS 123 velopment and expression, and fitness. The immune system is perhaps the most intensively studied complex regulatory system in biology. This chapter provided a glimpse of how it may be possible to link genetic vari- ation to immune regulatory control and its fitness consequences. The studies done so far focus on major polymorphisms. But it may soon be possible to study rare variants and their association with regulatory variability and susceptibility to different pathogens. This may lead to progress in linking quantitative genetic variability and the evolution of regulatory control systems. Immunological Variability of Hosts 9 Ahostoftenretainsimmunological memory of B and T cells stimulated by prior infections. Upon later inoculation, a host rapidly builds defense from its memory cells. Each host acquires a unique memory profile based on its infection history. In this chapter, I discuss the immune memory profiles of the host population. The following chapter describes how the structuring of im- munological memory in the host population shapes the structuring of antigenic variation in parasite populations. The first section reviews the immune processes that govern immuno- logical memory. I emphasize the rate at which a host can generate a secondary immune response and the rate at which immune memory decays. These rate processes determine how immunological memory imposes selective pressure on antigenic variants. The second section discusses the different consequences of immuno- logical memory for different kinds of parasites. For example, antibody titers tend to decay more rapidly in mucosal than in systemic locations. Thus, selective pressures on antigenic variation may differ for parasites that invade or proliferate in these different compartments. Cytopathic viruses, which kill their host cells, may be more susceptible to antibod- ies, whereas noncytopathic viruses may be more susceptible to CTLs that kill infected host cells. The different memory responses of anti- bodies and CTLs may impose different selective pressures on antigenic variation of cytopathic andnoncytopathic viruses. Thethird section describes the immunodominance of memory. The memory profile may differ from the pattern of immunodominance dur- ing primary infection. The immunodominance of memory affects the ease with which new parasite variants can spread.
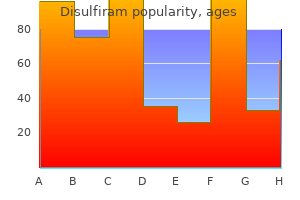
Order discount disulfiram on-line
Previous best responses can late deaths after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation symptoms nausea dizziness purchase 250 mg disulfiram. N Engl be re-achieved by resumption after imatinib discontinuation in J Med medications for anxiety generic 500 mg disulfiram fast delivery. Childs1 and Maria Berg1 1Section of Transplantation Immunotherapy treatment alternatives generic disulfiram 500 mg online, Hematology Branch, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD Recently, there has been a substantial gain in our understanding of the role that natural killer (NK) cells play in mediating innate host immune responses against viruses and cancer. Although NK cells have long been known to be capable of killing cancer cells independently of antigen recognition, the full therapeutic potential of NK cell–based immunotherapy has yet to be realized. Here we review novel methods to activate and expand human NK cells ex vivo for adoptive transfer in humans, focusing on the important phenotypic and functional differences observed among freshly isolated, cytokine activated, and ex vivo–expanded NK populations. Natural killer cell therapy for cancer: a new hope research investigating a variety of novel methods to bolster immu- nity against cancer through the use of adoptive NK cell infusions. Although NK cells inability to reliably expand large numbers of NK cells ex vivo have long been known to be capable of killing cancer cells precluded investigators from pursuing phase 1 trials evaluating for independently of antigen recognition, the full therapeutic potential an NK cell dose-response relationship. At present, it is not at all clear what threshold of NK cell numbers is needed to achieve an of NK cell–based immunotherapy has yet to be realized. Here we antitumor effect after adoptive NK cell transfer. Short- and long- review novel methods to activate and expand human NK cells term cell cultures containing cytokines without feeder cells, such as ex vivo for adoptive transfer in humans, focusing on the important IL-15 and IL-2, given alone or in combination with other growth phenotypic and functional differences observed among freshly factors, typically result in relatively small ex vivo NK cell expan- isolated, cytokine activated, and ex vivo–expanded NK populations. Although some investigators have observed differences in their growth rate, in our experience, NK cells obtained from cancer Ex vivo NK cell activation and expansion patients proliferate ex vivo similarly to those obtained from healthy donors. NK cells are defined by their CD3 /CD56 pheno- therapy remain in a proof-of-concept phase, with allogeneic infu- type, comprising 5% to 15% of circulating lymphocytes, and are sions often being given after immunosuppressive chemotherapy or commonly divided into CD56dimCD16 (90%) and CD56brightCD16 after an HLA-mismatched transplantation, most investigators have (10%) subpopulations with distinct effector functions. Recently, pursued methods to expand highly purified NK cells so that both the investigators have shown that NK cell tumor cytotoxicity can be efficacy and any toxicities of the infused product can be directly attributable to NK cells themselves. Recently, anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibod- Ex vivo cytokine-activated NK cells ies and the immunomodulatory drug lenalidomide were shown to Although culturing NK cells in cytokine-containing medium alone enhance both NK cell tumor trafficking and NK cell–mediated is less effective in expanding NK cells compared with cultures antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and cytokine re- containing feeder cells, such culture conditions are capable of lease against tumors while simultaneously suppressing regulatory activating NK cells quickly, even after a short overnight incubation, T cell function. Miller et al used a strategy of CD3 depletion of mononu- mediated cytotoxicity and TNF release against melanoma cells by clear cells (using the Miltenyi CliniMACS system) collected by Fc RIII (CD16) binding to antibody-bound tumor cells, as well as apheresis from haploidentical donors, followed by a brief 8- to through regulatory T cell inactivation. Further, recent advances in patients with relapsed hematological malignancies and solid in our ability to expand NK cells ex vivo have fueled translational tumors including breast cancer and ovarian cancer. Methods to activate and/or ex vivo expand human NK cells for infusion in patients with cancer. The addition of a CD56 selection after products before they could be used in the allogeneic setting. To medium containing nicotinamide (NAM), a specific inhibitor of avoid this complication, the University of Minnesota, which has the 38 NAD( )-dependent enzymes. In MEM medium supplemented most experience with the use of IL-2–activated NK cells, now incorporates both CD3 T-cell and CD19 B-cell depletion on with IL-2, IL-15, and NAM (at concentrations of 2. Remarkably, no medium changes or manipula- tion of the cell cultures were required during the 2-week expansion Ex vivo NK cell expansion without feeder cells process, with expanded cells containing a highly pure population of Some clinical studies of adoptive NK cell transfer have used 32 activated NK cells ( 95% CD3 /CD56 ). NK cells expanded short-term (12-18 hours) IL-2–activated NK cells. IL-2 alone using this approach underwent typical phenotypical and functional expands small numbers of NK cells, typically 10- to 20-fold after 14 changes observed with cytokine-induced NK cell activation, includ- days of cell culture, far less than murine studies predict would be ing up-regulation of TRAIL and enhanced cytotoxicity against needed to mediate antitumor effects in humans with cancer. Sutlu et K562 and other tumor cell lines, compared with fresh NK cells. These cells were activated ex vivo, being more ex vivo NK cell activation with cytokine-alone-containing medium. Expanded cell cultures contained 10% to 80% compared with NK cells expanded in medium without NAM, (average 38%) CD3 /CD56 NK cells with significant numbers of perhaps the consequence of CD62L up-regulation. Hematology 2013 235 Ex vivo NK cell expansion using feeder cells RCC cells) higher levels of IFN , IL-2, FasL, and TRAIL. The Several different methods (Figure 1) using feeder cells or APCs net effect of changes in NK cell phenotype and cytokine have been developed recently to expand large numbers of highly secretion resulted in expanded NK cells having markedly higher activated NK cells ex vivo, providing the opportunity to study the levels of cytotoxicity against K562 and various other tumor cell full potential of adoptive NK cell immunotherapy in humans.
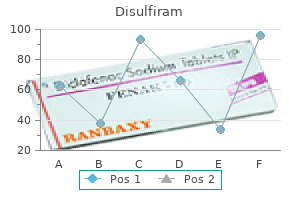
Citronella (Lemongrass). Disulfiram.
- How does Lemongrass work?
- What is Lemongrass?
- Dosing considerations for Lemongrass.
- Stomach and intestinal spasms, stomach ache, high blood pressure, convulsions, pain, vomiting, cough, rheumatism, fever, common cold, exhaustion, headache, use as an antiseptic and astringent, and other uses.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96704
Buy disulfiram paypal
Numerically more participants experienced dizziness in combination arm compared with either monotherapy arm; numerically more participants experienced hyperkalemia in combination arm compared with irbesartan arm inoar hair treatment best purchase for disulfiram. Combination of ACE-I and AIIRA compared with monotherapy with either ACE-I or AIIRA • Combination therapy of an ACE-I and an AIIRA compared with an ACE-I alone (4 trials) o Losartan and lisinopril compared with lisinopril alone (1 trial; fair quality): No differential effects found between groups for proteinuria reduction medications valium order disulfiram 250 mg overnight delivery. Markers for change in renal function were inconsistent; glomerular filtration rate was lower for those on combination therapy but there was no difference between groups in creatinine clearance medications knee discount disulfiram 250 mg buy. Creatinine clearance was stable in both groups, both trials. Harms were not delineated by treatment groups or were only delineated for an AIIRA. One dizziness/hypotension event occurred with ramipril monotherapy compared with zero with combination therapy; no hyperkalemia events occurred in either group. Harms were reportedly only for the combination therapy group. Changes in creatinine were numerically similar between groups. A numerical higher percent rate of hyperkalemia was seen in those on maximum dose combination therapy compared with lower dose combination therapy or monotherapy. Detailed assessment Monotherapy: Inter-class comparison of effectiveness, efficacy, and harms between AIIRA and ACE-I Proteinuric chronic kidney disease 83-95 We identified 17 trials that compared monotherapy with an angiotensin II receptor antagonist (AIIRA) to monotherapy with an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE-I). Trials rated as poor will not be discussed in detail, but additional information can be found in Evidence Table 10. Those trials that were rated poorly were heterogeneous in their flaws. Very high withdrawal rate was evident in 2 studies, 1 for a 99 98 withdrawal rate of 22%, and 1 with a withdrawal rate of 47%. The very high withdrawal rate in the latter, coupled with an overall small sample size (N=19, nine of which were withdrawn), 99 was the primary reason for its poor rating. In the former study, the poor rating stemmed from the lack of statistical analysis of any outcomes of interest and the lack of reporting of any adverse events in addition to the noted small sample size. A third study was rated as poor because the treatment arm groups were different at baseline in terms of both blood pressure and 97 proteinuria, and no adverse events were reported. The fourth trial that was rated poor quality 96 92 was the COOPERATE study, as was one of its sub-studies. This trial has been a point of much consternation and debate in the medical community; 1 correspondence raised concerns about statistical methods as well as better than expected level of similarity among treatment 100 groups at baseline. Recently, a formal retraction of the COOPERATE study was published by 101 the The Lancet. Per this retraction statement, a formal investigation of this trial conducted by the original university hospital revealed that this trial was not double blind, that the presence of a statistician during the data analysis was unclear, and that the patient specific data (on a sample chart review) could not be verified to be authentic. For this reason, the COOPERATE trial and its ambulatory blood pressure sub-study were rated as poor and were not included in this report. Valsartan was compared with lisinopril in 1 trial, to benazepril in 2 trials, and to 85, 95 87 ramipril in 2 trials. Telmisartan was compared with enalapril in 1 trial and irbesartan was 86 compared with fosinopril in 1 trial. We did not find any trials involving comparisons of either eprosartan or olmesartan to an ACE-I, or any trials involving comparisons of captopril, cilazapril, moexipril, or quinapril to an AIIRA. One trial reported a renal survival outcome, including time to end stage renal disease or 88 doubling of serum creatinine. All but 2 trials compared the change in level or percent of proteinuria experienced; the 2 trials that did not report changes in proteinuria did report changes 83, 94 in renal function and were included for the benefit of those analyses. Of note, while blood pressure control was not a primary outcome of interest in this analysis, blood pressure control is DRIs, AIIRAs, and ACE-Is Page 49 of 144 Final Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project known to impact proteinuria (with higher blood pressure leading to more proteinuria compared 106 with lower blood pressure). For that reason, if blood pressure control was reported as statistically not equivalent between groups, effects on proteinuria within that trial will not be considered to be independent of blood pressure control.
Syndromes
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
- Certain sexual practices (such as anal sex without a condom)
- Being infected while pregnant (the mother can pass the virus to the baby)
- Do not drink anything after midnight the day of your surgery. This includes water.
- Mitral regurgitation
- Damage to skeletal muscles
- Blood in your stool or black, tarry stools
- Excessive thirst
- Ligament sprains or tears (anterior cruciate, posterior cruciate, medial collateral and lateral collateral ligament tears)
- Stop for a day or two of rest for every 2,000 feet (600 meters) above 8,000 feet (2,400 meters)
Cheap disulfiram 250 mg with mastercard
No differences in the rate of myopathy or rhabdomyolysis when administering medications 001mg is equal to purchase cheap disulfiram line. Several factors might help explain the discrepant results of PROVE-IT and IDEAL: (1) All subjects in PROVE-IT had recent acute coronary syndrome treatment lice cheap disulfiram 250 mg otc, whereas only 11% of those in IDEAL had myocardial infarction within 2 months of randomization medicine 8 soundcloud purchase disulfiram 250 mg amex. This Statins Page 37 of 128 Final Report Update 5 Drug Effectiveness Review Project (2) The definition of the primary endpoint differed in the 2 trials. In IDEAL, the reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol with atorvastatin was slightly less than expected, and adherence in the atorvastatin group was not as good as in the 118 simvastatin group (89% compared with 95%). In a fair-quality, 1-year trial in patients with stable coronary artery disease, intensive atorvastatin (up to 80 mg, to a target of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol less than 80 mg/dL) was not more effective than a control group of diet plus low-dose lovastatin (5 mg if needed, to a target of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol less than 130 mg/dL) for reducing the number of ischemic episodes as measured on ambulatory electrocardiogram, patient-reported angina 119 frequency, and nitroglycerin consumption. There was a reduction in the number of ischemic episodes in both groups, but no difference between groups. There was no significant difference in major clinical events between groups after 1 year, but the number of events was small and the study was powered to detect a difference in ischemia, not clinical events. Placebo-controlled trials Many trials comparing a statin to placebo or, in a few instances, to non-pharmacologic treatments, reported health outcomes. These trials indicated which statins have been proven to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in various patient populations. This group included 27 118, 121-134 placebo-controlled trials and 2 head-to-head trials: 22 studies in outpatients 81, 117, and 7 studies in inpatients with acute myocardial infarction or unstable angina. Enrollment was in excess of 4000 patients with an average follow-up period of 5 years. All of the trials were good or fair quality and were considered the best evidence for demonstrating a reduction in cardiovascular health outcomes with statins. These included studies of patients hospitalized with acute myocardial infarction or unstable angina. There was 1 head-to-head trial of intensive atorvastatin therapy compared with a standard dose of pravastatin. Six other trials compared a statin to placebo or usual care. In these trials, coronary heart disease events or cardiovascular morbidity and mortality was reported either as a secondary endpoint or incidentally (that is, even though it was not a predefined endpoint). In general, these studies had 148, 155 insufficient power to assess coronary heart disease events. Only 2 of these trials Statins Page 38 of 128 Final Report Update 5 Drug Effectiveness Review Project enrolled more than 500 patients. The others ranged from 151 to 460 included patients. As evidence regarding reduction in coronary heart disease events, these trials were fair or fair-to-poor in quality. Three additional trials with clinical outcomes did not fit the 65, 166, 167 criteria for the other categories. Studies with primary coronary heart disease endpoints The major trials are summarized briefly in Tables 9 (outpatient studies) and 11 (inpatient studies) below and in more detail in Evidence Table 2. Statins Page 39 of 128 Final Report Update 5 Drug Effectiveness Review Project Table 9. Outpatient and community-based placebo-controlled trials of statins with coronary heart disease endpoints Number needed to Risk status/ Reduction in treat to Average annual Baseline Study coronary events prevent a Trial event rate in LDL duration % LDL (relative risk coronary a b (Quality) placebo group (mg/dL) (years) reduction reduction) event Trials of atorvastatin 171, 172 ASCOT HTN plus CHD risk Atorvastatin factors/ 133 3. Studies in outpatients Primary prevention AFCAPS (lovastatin), WOSCOPS (pravastatin), and JUPITER (rosuvastatin) trials recruited 81, 126, 132 patients without a history of coronary heart disease (primary prevention). One new trial was rated poor quality due to multiple methodologic weaknesses. Statins Page 41 of 128 Final Report Update 5 Drug Effectiveness Review Project 132 In WOSCOPS, pravastatin 40 mg reduced coronary events by 31%, or 1 for every 44 patients (men only) treated (absolute risk, 5. WOSCOPS used a stricter definition of coronary events, defined as the occurrence of nonfatal myocardial infarction or coronary heart disease death, than AFCAPS, which included incidence of unstable angina in their primary outcome, so the relative risk reductions and numbers-needed- to-treat were not directly comparable. In WOSCOPS, but not AFCAPS/TexCAPS, pravastatin therapy reduced coronary disease deaths by 33% (95% CI, 1 to 55) and all-cause mortality by 22% (95% CI, 0 to 40), a result that nearly reached statistical significance (P=0.
Discount disulfiram american express
Comparison of esomeprazole enteric-coated capsules vs esomeprazole magnesium in the treatment of active duodenal ulcer: a randomized medicine rocks state park buy cheap disulfiram 500 mg on line, double-blind 4d medications disulfiram 250 mg order with mastercard, controlled study medications reactions order discount disulfiram on line. Dekkers CP, Beker JA, Thjodleifsson B, Gabryelewicz A, Bell NE, Humphries TJ. Efficacy and safety of lansoprazole in the treatment of gastric ulcer: A multicentre study. A comparative study on endoscopic ulcer healing of omeprazole versus rabeprazole with respect to CYP2C19 genotypic differences. Comparison of the efficacy of rabeprazole 10 mg and omeprazole 20 mg for the healing rapidity of peptic ulcer diseases. Proton pump inhibitors Page 80 of 121 Final Report Update 5 Drug Effectiveness Review Project 110. Double blind comparative study of omeprazole and ranitidine in patients with duodenal or gastric ulcer: a multicentre trial. The effect of omeprazole and ranitidine on ulcer healing, relief of symptoms, and incidence of adverse events in the treatment of duodenal ulcer patients. Omeprazole compared with ranitidine once daily in the treatment of duodenal ulcer. A comparison of omeprazole and ranitidine for duodenal ulcer in South African patients. Omeprazole provides quicker symptom relief and duodenal ulcer healing than ranitidine. Double-blind comparison of lansoprazole, ranitidine and placebo in the treatment of acute duodenal ulcer. Improved symptom relief and duodenal ulcer healing with lansoprazole, a new proton pump inhibitor, compared with ranitidine. Cremer M, Lambert R, Lamers CB, Delle Fave G, Maier C. A double-blind study of pantoprazole and ranitidine in treatment of acute duodenal ulcer. Pantoprazole and ranitidine in the treatment of acute duodenal ulcer. Comparison of pantoprazole and ranitidine in the treatment of acute duodenal ulcer. Rabeprazole is superior to ranitidine in the management of active duodenal ulcer disease: results of a double-blind, randomized North American study. Multicenter double-blind comparative study with ranitidine. Bardhan KD, Bianchi Porro G, Bose K, Daly MJ, Hinchliffe RF, Jonsson E. A comparison of two different doses of omeprazole versus ranitidine in the treatment of duodenal ulcers. Omeprazole vs ranitidine in the healing of duodenal ulcer. A multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled study of omeprazole versus ranitidine in the treatment of duodenal ulcer in Israel. Proton pump inhibitors Page 81 of 121 Final Report Update 5 Drug Effectiveness Review Project 125. Crowe JP, Wilkinson SP, Bate CM, Willoughby CP, Peers EM, Richardson PD. Symptom relief and duodenal ulcer healing with omeprazole or cimetidine. Opus (Omeprazole Peptic Ulcer Study) Research Group. Davis RH, Stott NC, Barber JH, Freeling P, Peers EM, Richardson PD.
Buy cheap disulfiram 500 mg on line
The data from this stage of a trial are only occasionally of value but can serve a valuable role in screening out ineligible or non-compliant participants xerogenic medications cheap disulfiram 500 mg with visa, in ensuring that participants are in a stable condition medicine buddha buy 500 mg disulfiram free shipping, and in providing baseline observations medicine 360 disulfiram 500 mg purchase fast delivery. A run-in period is sometimes called a washout period if treatments that participants were using before entering the trial are discontinued. This term (or the term ‘‘safe’’) should not be used when evidence on harms is simply absent or is insufficient. Sample size: The number of people included in a study. In research reports, sample size is usually expressed as "n. Larger sample sizes also increase the chance that rare events (such as adverse effects of drugs) will be detected. Sensitivity analysis: An analysis used to determine how sensitive the results of a study or systematic review are to changes in how it was done. Sensitivity analyses are used to assess how robust the results are to uncertain decisions or assumptions about the data and the methods that were used. Side effect: Any unintended effect of an intervention. Side effects are most commonly associated with pharmaceutical products, in which case they are related to the pharmacological properties of the drug at doses normally used for therapeutic purposes in humans. Standard deviation (SD): A measure of the spread or dispersion of a set of observations, calculated as the average difference from the mean value in the sample. Standard error (SE): A measure of the variation in the sample statistic over all possible samples of the same size. The standard error decreases as the sample size increases. Standard treatment: The treatment or procedure that is most commonly used to treat a disease or condition. In clinical trials, new or experimental treatments sometimes are compared to standard treatments to measure whether the new treatment is better. Statistically significant: A result that is unlikely to have happened by chance. Study: A research process in which information is recorded for a group of people. The data are used to answer questions about a health care problem. Study population: The group of people participating in a clinical research study. The study population often includes people with a particular problem or disease. It may also include people who have no known diseases. Subgroup analysis: An analysis in which an intervention is evaluated in a defined subset of the participants in a trial, such as all females or adults older than 65 years. Superiority trial: A trial designed to test whether one intervention is superior to another. Surrogate outcome: Outcome measures that are not of direct practical importance but are believed to reflect outcomes that are important; for example, blood pressure is not directly important to patients but it is often used as an outcome in clinical trials because it is a risk factor for stroke and heart attacks. Surrogate endpoints are often physiological or biochemical markers that can be relatively quickly and easily measured, and that are taken as being predictive of important clinical outcomes. They are often used when observation of clinical outcomes requires long follow-up. Long-acting opioid analgesics 53 of 74 Final Update 6 Report Drug Effectiveness Review Project Survival analysis: Analysis of data that correspond to the time from a well-defined time origin until the occurrence of some particular event or end-point; same as time-to-event analysis. Systematic review: A review of a clearly formulated question that uses systematic and explicit methods to identify, select, and critically appraise relevant research and to collect and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The extent to which a drug’s adverse effects impact the patient’s ability or willingness to continue taking the drug as prescribed. These adverse effects are often referred to as nuisance side effects, because they are generally considered to not have long-term effects but can seriously impact compliance and adherence to a medication regimen.
Ali, 27 years: Identification of performance gaps A performance gap is the variation between the Define criteria and standards current performance and the performance accord- ing to standards.
Oelk, 25 years: O verview ofincluded system aticreviews onskeletalm uscle relaxants A uth or Skeletalm uscle N um berofincluded Y ear Purpose ofstudy relaxants evaluated studies and patients Q uality M ainfindings System aticreviews vanTulder A ssess th e effectiveness Tiz anidine 30 trials (3 cyclobenz aprine G ood.
Moff, 34 years: Table 1 summarizes the pharmacology, dosing, and indications of the current disease- modifying drug treatments options for multiple sclerosis.
Merdarion, 60 years: Across the 3 studies, response 93 94 rates with lamotrigine ranged from 45% in adjunct treatment to 68 in monotherapy but were not statistically significantly different from placebo or other regimens.
Marlo, 36 years: Proton pump inhibitors Page 83 of 121 Final Report Update 5 Drug Effectiveness Review Project 154.
Stejnar, 35 years: These still die of opportunistic previously hidden infections and mounts an im- infections with severe suffering and stigmatization.
Khabir, 45 years: York, UK: NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination; 2001.
Cronos, 52 years: The and recruit elements required for transcription.
Asaru, 23 years: R CT = R andom ControlledTrial,U TI = U rinaryTractInfection,N S = N ostatisticaldifference Overactive bladder 4 of 217 Final Report Update 4 Drug Effectiveness Review Project Evidence Table 1.
Sanuyem, 37 years: The prozone phenomenon with syphilis and HIV-1 co-infection.
8 of 10 - Review by T. Marcus
Votes: 60 votes
Total customer reviews: 60
References
- Shih IM, Wang TL, Traverso G, et al. Top-down morphogenesis of colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(5):2640-2645.
- Maltby JR, et al. LMA-Classic and LMA-ProSeal are effective alternatives to endotracheal intubation for gynecologic laparoscopy. Can J Anaesth. 2003;50(1):71-77.
- Bruhlmann W, Weishaupt D, Goebel N, Imhof E. Therapeutic embolization of a systemic arterialization of lung without sequestration. Eur J Radiol 1998;8:355-8.
- Baker JR, Metcalf PA, Holdaway IM, Johnson RN. Serum fructosamine concentration as measure of blood glucose control in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1985;290:352-355.