Anita Deswal, MD, MPH
- Associate Professor of Medicine
- Section of Cardiology and Winters
- Center for Heart Failure Research
- Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center and Baylor College of Medicine
- Houston, Texas
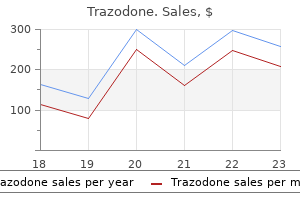
Trazodone dosages: 100 mg
Trazodone packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Buy cheap trazodone 100 mg
The lowest quarter of values lie below the lower quartile or 25th percentile symptoms 8 days past ovulation discount 100 mg trazodone visa, the Review of basic statistics 101 lower half below the 50th percentile medicine 8 - love shadow purchase trazodone with a visa, and the lowest three-quarters below the upper quartile or 75th percentile treatment lupus cheap trazodone online. The interquartile range is the range of values from the 25th to the 75th percentile values. It is the average of the squares of the difference between each value and the mean or the sum of the squares of the difference between each value and the mean divided by n (the number of data points in the sample). Populations and samples A population is the set of all possible members of the group being studied. The members of the population have various attributes in common and the more characteristics they have in common, the more homogeneous and therefore restrictive the population. An example of a fairly restricitive population would be all white males between 40 and 65 years of age. With a restrictive population, the generalizability of the population is often a problem. The less the members of the sample have in common, the more generalizable the results of data gath- ered for that population. For example, a population that included all males is more generalizable than one that only includes white males between 40 and 65 years of age. An example could be all white males available to the researcher on a given day for a study. Reasons to use a sample rather than the entire population include convenience, time, cost,andlogistics. The sample may or may not be representative of the entire population, an issue which has been discussed in the chapter on sources of bias (Chapter 8). Histograms or frequency polygons show how many subjects in a sample or population (the y-axis) have a certain characteristic value (the x-axis). When plotted in this manner, we call the graph a distribution of values for the given sample. By definition, a symmet- rical distribution is one for which the mean, median, and mode are identical. They are said to be skewed to the right (positive 102 Essential Evidence-Based Medicine Fig. Skew should be discussed when presenting and evaluating data and the range of the data given in addition to the standard measures of central tendency and dispersion. One clue to the presence of skewed data is if twice the standard deviation is larger than the mean. The mathematical measures used to describe data are different for skewed distributions than for symmetrical ones. Abraham de Moivre, a French mathematician, discovered it about 50 years before Gauss published his thesis. It is a special case of a symmetrical distribution, and it describes the frequency of occurrence of many naturally occurring phenomena. For the purposes of most statistical tests, we assume normality in the distribution of a variable. It is better defined by giving its properties: (1) The mean, median, and mode are equal so that we can say that the curve is symmetric around the mean and not skewed or has a skew = 0. There are specific numerical equivalents to the standard deviations of the nor- mal distribution, as shown in Table 9. The normal distribution is the basis of most statistical tests and concepts we will use in critical interpretation of the statistics used in the medical literature. Percentages Percentages are commonly used in reporting results in the medical literature. Percentage improvement or percentage of patients who achieve one of two dichotomous endpoints are the preferred method of reporting the results. A percentage is a ratio or fraction, the numer- ator divided by the denominator, multiplied by 100 to create a whole number. Obviously, inaccuracies in either the numerator or denominator will result in inaccuracy of the percentage. Percentofapercent will usually show a very large result, even when there is only a small absolute change in the variables.
100 mg trazodone purchase with mastercard
Am J tion on intestinal permeability and the development of multiple organ Gastroenterol 2007 treatment lupus order trazodone overnight; 102:412–429 medications hard on liver proven trazodone 100 mg; quiz 468 failure after multiple injury treatment 8th feb trazodone 100 mg buy visa. N Engl J Med 2011; 365:506–517 with an immune-enhancing diet in patients with severe head injuries. Pupelis G, Selga G, Austrums E, et al: Jejunal feeding, even when 27:2799–2805 instituted late, improves outcomes in patients with severe pancreati- 446. Intensive Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee: Canadian clinical practice Care Med 2005; 31:524–532 guidelines for nutrition support in mechanically ventilated, critically ill 450. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2004; provided within 24 h of injury or intensive care unit admission, 10:89–96 signifcantly reduces mortality in critically ill patients: A meta-anal- 451. Radrizzani D, Bertolini G, Facchini R, et al: Early enteral immunonu- ysis of randomised controlled trials. Bertolini G, Iapichino G, Radrizzani D, et al: Early enteral immunonu- tion on clinical outcome in mechanically ventilated patients suffering trition in patients with severe sepsis: Results of an interim analysis head injury. Singer P, Theilla M, Fisher H, et al: Beneft of an enteral diet enriched J Surg Res 2010; 161:288–294 with eicosapentaenoic acid and gamma-linolenic acid in ventilated 455. Crit Care Med 2006; 34:1033–1038 tion of a formula (Impact) supplemented with arginine, nucleotides, 474. The effect Clinical Trials Network: Enteral omega-3 fatty acid, gamma-linolenic on nosocomial infections and outcome. Grau-Carmona T, Morán-García V, García-de-Lorenzo A, et al: Effect serious illness: A systematic review of the evidence. Crit Care Med of an enteral diet enriched with eicosapentaenoic acid, gamma-lin- 2002; 30:2022–2029 olenic acid and anti-oxidants on the outcome of mechanically venti- 460. Avenell A: Glutamine in critical care: Current evidence from system- lated, critically ill, septic patients. Jiang H, Chen W, Hu W, et al: [The impact of glutamine-enhanced parenteral nutrition of critically ill medical patients: A randomised enteral nutrition on clinical outcome of patients with critical illness: A controlled trial. Intensive Care Med 2008; 34:1411–1420 systematic review of randomized controlled trials]. Current evidence and markers, and clinical outcomes in septic patients: A randomized, ongoing trials on the use of glutamine in critically-ill patients and controlled clinical trial. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2006; ety; European Respiratory Society; European Society of Intensive 18:616–618 Care Medicine; Society of Critical Care Medicine; Sociètède Rèani- 464. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2006; Critical Care: Brussels, Belgium, April 2003: executive summary. Wernerman J, Kirketeig T, Andersson B, et al; Scandinavian Critical 30:76–83 Care Trials Group: Scandinavian glutamine trial: A pragmatic multi- centre randomised clinical trial of intensive care unit patients. Crit Care nyl-L-glutamine-supplemented parenteral nutrition improves infec- Med 2010; 38:1765–1772 tious morbidity in secondary peritonitis. Am J pharmaconutrients improves Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Respir Crit Care Med 2009; 179:48–53 score in critically ill patients with sepsis: Outcome of a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Intensive Care Med 2009; 35:623–630 ratory distress syndrome: A meta-analysis of outcome data. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009; 180:853–860 oxidants in mechanically ventilated patients with severe sepsis and 489. Bertolini G, Boffelli S, Malacarne P, et al: End-of-life decision-making septic shock. Intensive Care Med 2010; 36:1495–1504 with eicosapentaenoic acid, gamma-linolenic acid, and antioxidants 490. Am haemodynamic support guidelines for paediatric septic shock: An J Hosp Palliat Care 2009; 26:295–302 outcomes comparison with and without monitoring central venous 492. Lautrette A, Darmon M, Megarbane B, et al: A communication strat- oxygen saturation. Acta Clin Belg Suppl Critical Care Medicine Task Force 2004-2005, Society of Critical 2007; Suppl:44–59 Care Medicine: Clinical practice guidelines for support of the fam- 514. Am J omy for abdominal compartment syndrome in children: Before it is Respir Crit Care Med 2008; 178:269–275 too late. Pediatr Crit Care Med for the acquisition of bloodstream infections with extended-spectrum 2009; 10:562–570 beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species in 499. Vanguard Center Contributors: World Federation of Pediatric Inten- J Hosp Infect 2008; 68:108–115 sive Care and Critical Care Societies: Global Sepsis Initiative. Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A; International Consensus Confer- 2007; 26:1128–1132 ence on Pediatric Sepsis: International pediatric sepsis consensus 519.
Generic trazodone 100 mg buy on-line
Weight loss with increased or normal appetite Graves’ disease is an autoimmune thyroid disease medicine in the 1800s trazodone 100 mg with mastercard. Proptosis (exophthalmos) with lid retraction medications you cant donate blood purchase cheap trazodone, stare and Sex lid lag are prominent features medicine rock order trazodone amex, and in its most severe F > M form it may cause sight loss due to damage to the optic nerve. Thyroid dermopathy (also called pretibial myxoedema) r Fifteen per cent of patients have a close relative with is a thickening or ‘orange-peel appearance’ of the skin, Graves’, and 50% of relatives have circulating thyroid most often affecting the lower leg. Microscopy The thyroid epithelial cells are increased in number and size with large nuclei. This causes a generalised, uncontrolled stimulation lymphocyte infiltration may also be seen. After many years the gland becomes non-functional and Investigations the patient becomes hypothyroid. Other complica- is made by a combination of clinical features and detec- tions of Graves’ disease may also be due to similar tion of thyroid autoantibodies. Thesecomplicationsdonotresolveontreat- Management ment to reduce the overactivity of the thyroid. Antithyroid drugs (usually carbimazole) are given to r Some symptoms of Graves’ disease relate to apparent suppress the gland. Graves’ disease commonly enters catecholamine (noradrenaline and adrenaline) excess, remission after 12–18 months, so a trial of withdrawal for example tachycardia, tremor and sweating. Patients who are severely symptomatic roid hormones induce cardiac catecholamine recep- with hyperthyroidism also benefit from β-blockers. Subtotal thyroidectomy results in normali- Primary Idiopathic/autoimmune thyroid atrophy sation of thyroid function in 70%. The patient must be made Iatrogenic: radioactive iodine, surgery, drugs euthyroid before surgery with antithyroid drugs and β- Iodine deficiency (common in Nepal, Bangladesh) blockers (see page 436). Inborn errors of hormone synthesis Secondary Panhypopituitarism due to pituitary adenoma Iatrogenic: pituitary ablative therapy/surgery Prognosis Tertiary Hypothalamic dysfunction (rare) Thirty to fifty per cent of patients used to undergo spon- Peripheral resistance to thyroid hormone (rare) taneous remission without treatment. Hypothyroidism (myxoedema) Thyrotoxic crisis (storm) Definition Definition Hypothyroidism is a clinical syndrome resulting from a Arare syndrome of severe acute thyrotoxicosis, which deficiency of thyroid hormones. Pathophysiology Congenital hypothyroidism causes permanent develop- Pathophysiology mental retardation. In children it causes reversible de- Levels of thyroid-binding protein in the serum fall and layedgrowthandpuberty,anddevelopmentaldelay. This results in increased cocious puberty may occur in juveniles, due to pituitary free T3 and T4, coupled to increased sensitivity of the hypertrophy. In adults it causes decreased removal of heart and nerves due to the presence of catecholamines. The symptoms include life-threatening coma, heart fail- ure and cardiogenic shock. There is a high fever (38– Clinical features 41◦C), flushing and sweating, tachycardia, often with Usually insidious onset. Central nervous creasing lethargy, forgetfulness, intolerance to cold, symptoms include agitation, restlessness, delirium and weight gain, constipation and depression (see also coma. Hypercholesterolaemia increases the incidence of tithyroid drugs and corticosteroids. Chapter 11: Thyroid axis 433 r Respiratory system: Respiration may be slow and shal- Aetiology low. Patients have detectable anti-microsomal antibody and r Gastrointestinal system: Reduced peristalsis, leading antithyroglobulin antibodies in most cases. The patient, typically a postmenopausal female, presents r Other signs include a cool rough dry skin, hair loss, with a diffuse goitre. Although most patients are euthy- puffy face and hands, a hoarse husky voice and slowed roid, thyrotoxicosis can occur and if presentation is late, reflexes. The thyroid is diffusely enlarged and has a fleshy white cut surface due to lymphocytic infiltration, which is seen Investigations on microscopy around the destroyed follicles. Thyroid autoantibodies are High titres of circulating antithyroid antibodies, associ- present in patients with autoimmune disease.
Discount trazodone online amex
High n-9 Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Diets There are limited data on the adverse health effects from consuming high levels of n-9 monounsaturated fatty acids (see Chapter 8 medications for rheumatoid arthritis discount trazodone 100 mg buy on-line, “Tolerable Upper Intake Levels”) schedule 8 medicines trazodone 100 mg order free shipping. Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range n-9 Monounsaturated fatty acids are not essential in the diet medications given for uti order 100 mg trazodone with visa, and the evidence relating low and high intakes of monounsaturated fatty acids and chronic disease is limited. Many populations of the world, such as in Crete and Japan, have low total intakes of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (e. However, high intakes of n-6 polyunsaturated fats have been associated with blood lipid profiles (e. An inverse association between linoleic acid intake and risk of coronary death was observed in several prospective studies (Arntzenius et al. Controlled trials have examined the effects of sub- stituting n-6 fatty acids in the diet to replace carbohydrate or saturated fatty acids (Mensink et al. Risk of Diabetes A number of epidemiological studies have been conducted to ascer- tain whether the quality of fat can affect the risk for diabetes. An inverse relationship was reported for vegetable fats and polyunsaturated fats and risk of diabetes (Colditz et al. One study reported a positive association between 2-hour glucose concentrations and polyunsaturated fatty acid intake (Mooy et al. A review of epidemiological studies on this relationship concluded that higher intakes of polyunsaturated fats could be beneficial in reducing the risk for diabetes (Hu et al. Risk of Nutrient Inadequacy Dietary n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids have been reported to contrib- ute approximately 5 to 7 percent of total energy intake of adults (Allison et al. Oxidation products of lipids and proteins are found in athero- sclerotic plaque and in macrophage foam cells. Risk of Inflammatory Disorders There has been significant interest in the use of dietary n-6 fatty acids to modulate inflammatory response. The ∆6 desaturase enzyme is the initial step in desaturation of linoleic acid to arachidonic acid (see Figure 8-1). Epidemiological studies, however, suggest that n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids are not associated (or have an inverse relationship) with cancer. Howe and coworkers (1990) analyzed 12 case- control studies conducted prior to 1990 and determined that the relative risk of breast cancer for an increment of 45 g of polyunsaturated fat per day was only 1. More recent case-control and prospective studies fur- ther support the minimal effect of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on breast cancer risk (Männistö et al. A similar relation- ship has been reported for linoleic acid intake and prostate cancer (Giovannucci et al. The range of intake of polyunsaturated fat was sufficiently large in these combined studies to comfortably conclude that the epidemiological evi- dence largely contradicts the animal studies; at least to date, no association between polyunsaturated fat, mainly n-6 fatty acids, and risk of breast cancer has been detected. Furthermore, in a review of the literature and meta-analyses of case-controlled and prospective epidemiological studies, Zock and Katan (1998) concluded that it was unlikely that high intakes of linoleic acid substantially raise the risk of breast, colorectal, or prostate cancer. Risk of Nutrient Excess High intakes of linoleic acid can inhibit the formation of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids from α-linolenic acid, which are precursors to the important eicosanoids (see Chapter 8). Many of the epidemiological studies used fish or fish oil intake as a surrogate for n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake. The amounts of n-3 fatty acids vary greatly in fish, however, and unless the amounts of n-3 fatty acids are known, any conclusions are open to question. Furthermore, other components in fish may have effects that are similar to n-3 fatty acids and therefore may confound the results. A similar result was found in Rotterdam that compared older people who ate fish with those who did not (Kromhout et al. In the Physicians’ Health Study, eating fish once per week decreased the relative risk of sudden cardiac death by 52 percent compared with eating fish less than once per month (Albert et al. In this study, although dietary total n-3 fatty acid intake correlated inversely with total mortality, no effect on total myocardial infarction, nonsudden cardiac death, or total cardiovascular mortality was observed. After adjustment for classical risk factors, the reduction was only 32 percent and no longer significant. There are fewer data with regard to the effects of fish and n-3 poly- unsaturated fatty acids on stroke. In the Zutphen Study, consumption of more than 20 g/d of fish was associated with a decrease in the risk of stroke (Keli et al. In contrast, in the Chicago Western Electric Study and the Physicians’ Health Study, fish intake was not signifi- cantly associated with decreased stroke risk (Morris et al. Some studies, however, did not show an effect on platelet aggregation after the consumption of 4.
Order trazodone 100 mg without a prescription
The first is a framework of measures medications side effects prescription drugs buy trazodone 100 mg on line, strategies and process improvements for health care systems and end users [3] treatment quality assurance unit 100 mg trazodone buy overnight delivery. The three measures are justification symptoms 4 weeks pregnant trazodone 100 mg buy visa, optimization and error minimization, which are used along the patient journey. For the realization of any action, it is important to narrow the gaps between knowledge and practice. Each step of an action requires the contribution from different stakeholders who play unique roles. Effective advocacy improves the probability of policy adoption and use by practitioners. Under this radiation protection framework, a range of implementation strategies is used. Research includes conducting population exposure surveys and procedure exposure in facilities. The strengthening of advocacy, awareness, training, workforce capacity, physical infrastructure, policies, evaluation and ongoing improvement apply to health care systems and end users. There is synergy between these strategies and collectively they add value to each other. The common vehicles supporting these actions are evidence based recommendations and tools. Keeping these tools current; matching the contents to the setting; improving their user friendliness, format, media and search function; and securing end user support will lead to better acceptance and use. All actions are interrelated and synergy should be sought to maximize the outcome. Based on the findings of population and procedure exposure surveys, improvement actions should follow. Similarly laboratory developed quality control measures should be integrated into daily practice when appropriate. One of the issues limiting the development and implementation of these actions is the availability of human and financial resources. To maximize resources and synergy, and to minimize duplication, collaboration under an integrated framework is useful. A global platform such as this forum, the International Action Plan for the Radiological Protection of Patients [4], the International Basic Safety Standards [5], the World Health Organization’s Global Initiative on Radiation Safety in Healthcare Settings [6] and the global referral guidelines project [7] facilitate leader and stakeholder engagement across disciplines and sectors, communication, collaboration, team building, innovation, development of a safety culture and resource mobilization. Using a framework such as the one discussed, together with good teamwork, will overcome many of the emerging challenges and narrow the gaps between evidence and practice. These actions will improve patient care through doing the right procedure (justified) and doing the procedure right (optimized and without error), each time. Most principles for dose reduction in screen-film radiography, including justification, are relevant to digital systems. However, digital systems have the potential to significantly increase patient dose, possibly due to lack of awareness among imaging personnel. Examination parameters, such as tube voltage, tube current and filtration, have been adopted from screen-film technology without further adjustments. The imaging parameters must be optimized according to the best performance of a particular system. Current safety issues with clinical digital radiography are discussed; these are technology factors, such as automatic exposure factors and exposure index; and human factors, such as inappropriate exposure, no collimation and overexposure. Therefore, implementation of dose indicators and dose monitoring is mandatory for digital radiography in practice. Finally, the advantages and challenges of radiographer performed fluoroscopy will also be discussed. Most principles for dose reduction in screen-film radiography, including justification, are still relevant to digital systems. However, in digital systems, different scenarios apply for dose reduction and optimization compared with screen-film radiography [1–3].
Purchase line trazodone
The pretest probability is converted to pretest odds and multiplied by the likelihood ratio medications excessive sweating quality 100 mg trazodone. This results in the post-test odds medicine bag discount generic trazodone uk, which are converted back to a probability medications causing gout discount 100 mg trazodone visa, the post-test probability. The end result of using Bayes’ theorem when a positive test occurs is the post- test probability of disease. For a negative test, Bayes’ theorem calculates the probability that the person still has disease even if a negative test occurs. In this case, a urine culture was done on all the children and therefore was the gold standard. In the study population, the probability of a urinary tract infection in the children being evaluated in that setting was 0. Clinical evaluation of a rapid screening test for urinary tract infections in children. In other words, a positive urine dipstick has increased the prob- ability of a urinary tract infection from 0. Using the same example for a negative test: (1) Pretest probability and odds of disease are unchanged. In other words, a negative urine dipstick has reduced the probability of uri- nary tract infection from 0. Of course, it is important to recognize that the pretest probabil- ity of not having a urinary tract infection before doing any test was estimated at 90%. Should we do the urine culture or gold standard test for all children who have a nega- tive dipstick test in order to pick up the 6% who actually have an infection? This conundrum must be accurately communicated to the patient, and in this case the parents, and plans made for all contingencies. Choosing to do the urine cul- ture on all children with a negative test will result in a huge number of unneces- sary cultures. They are expensive and will result in a large expenditure of effort and money for the health-care system. Whether or not to do the urine culture depends on the consequences of not diagnosing an infection at the time the child presents with their initial symptoms. In the office, it is not known if these unde- tected children progress to kidney damage. The available evidence suggests that there is no significant delayed damage, that the majority of these infections will spontaneously clear or the child will show up with persistent symptoms and be treated at a later time. Connect these two points, and continue the line until the post-test probability is reached. For our example of a child with signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection, the plot of the post-test probability for this clinical situation is shown in Fig. Calculating post-test probabilities using sensitivity and specificity directly The other way of calculating post-test probabilities uses sensitivity and speci- ficity directly to calculate the predictive values. Not only are positive and nega- tive predictive values of the test related to the sensitivity and specificity, but they are also dependent on the prevalence of disease. The prevalence of disease is the 268 Essential Evidence-Based Medicine. Simply knowing the sensitivity and speci- ficity of a test without knowing the prevalence of the disease in the population from which the patient is drawn will not help to differentiate between disease and non-disease in your patient. Clinicians can use pretest probability for disease and non-disease respectively along with the test sensitivity and specificity to calculate the post-test probability that the patient has the disease (post-test probability = predictive value). Calculating predictive values step by step (1) Pick a likely pretest probability (P) of disease using the rules we discussed in Chapter 20. Moderate errors in the selection of this number will not signifi- cantly affect the results or alter the interpretation of the result. Let’s go back to the 156 young children with diarrhea whom we met at the end of Chapter 23. We have already decided that this study population does not represent all children with diarrhea who present to a general pediatrician’s office. In this setting, the pediatrician estimates the prevalence of bacterial diarrhea is closer to 0.
Generic trazodone 100 mg overnight delivery
Finally treatment uti purchase trazodone 100 mg with amex, the new reliance on electronic searching methods has increased the role of the health sciences librarian who can provide guidance and assis- tance in the searching process and should be consulted early in the process treatment lyme disease buy discount trazodone on line. Databases and websites are updated frequently and it is the librarian’s role to maintain a competency in expert searching techniques to help with the most difficult searching challenge medications for ocd buy trazodone 100 mg otc. Pierre Pachet, Professor of Physiology, Toulouse University, 1872 Learning objectives In this chapter you will learn: r the unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses of common clinical research study designs r descriptive – cross-sectional, case reports, case series r timed – prospective, retrospective r longitudinal – observational (case–control, cohort, non-concurrent cohort), interventional (clinical trial) r the levels of evidence and how study design affects the strength of evidence. Since various research study designs can accomplish different goals, not all studies will be able to show the same thing. Therefore, the first step in assessing the validity of a research study is to determine the study design. The ability to prove causation and expected potential biases will largely be determined by the design of the study. Identify the study design When critically appraising a research study, you must first understand what dif- ferent research study designs are able to accomplish. Characterizations in this manner, or so-called timed studies, have traditionally been divided into prospec- tive and retrospective study designs. Prospective studies begin at a time in the past and subjects are followed to the present time. Retrospective studies begin at the present time and look back on the behavior or other characteristics of those subjects in the past. These are terms which can easily be used incorrectly and misapplied, and because of this, they should not be referred to except as gener- alizations. As we will see later in this chapter, “retrospective” studies can be of several types and should be identified by the specific type of study rather than the general term. Descriptive studies Descriptive studies are records of events which include studies that look at a series of cases or a cross-section of a population to look for particular charac- teristics. These are often used after several cases are reported in which a novel treatment of several patients yields promising results, and the authors publishing the data want other physicians to know about the therapy. Case reports describe individual patients and case series describe accounts of an illness or treatment in a small group of patients. In cross-sectional studies the interesting aspects of a group of patients, including potential causes and effects, are all observed at the same time. Case reports and case series Case reports or small numbers of cases are often the first description of a new disease, clinical sign, symptom, treatment, or diagnostic test. They can also be a description of a curriculum, operation, patient-care strategy, or other health- care process. Some case reports can alert physicians to a new disease that is about to become very important. One series con- sisted of two groups of previously healthy homosexual men with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, a rare type of pneumonia. These diseases had previously only been reported in people who were known to be immunocompromised. It quickly became evident as more clinicians noticed cases of these rare diseases. Since most case reports are descriptions of rare diseases or rare presenta- tions of common diseases, they are unlikely to occur again very soon, if ever. To date, physicians have not been deluged with a rash of young methamphetamine users with strokes. Therefore, case reports are a useful venue to report unusual symptoms of a common illness, but have limited value. New treatments or tests described in a study without any control group also fall under this category of case reports and case series. At best, these descriptive studies can suggest future directions for research on the treatment or test being reported. They are cheap, relatively easy to do with existing medical records, and potential clini- cal material is plentiful. If you see new presentations of disease or interesting cases, you can easily write a case report. These studies do not provide explanations and cannot show asso- ciation between cause and effect. Since no comparison is made to any control group, contributory cause cannot be proven. A good general rule for case studies is to “take them seriously and then ignore them.
Buy discount trazodone 100 mg
Individual schools can also select additional learning outcomes in order to develop or preserve a distinct educational profle – for example medications made from animals 100 mg trazodone buy otc, a specifc emphasis on research-related experience and skills - without compromising the essential competence of their graduates and their ftness to care for patients symptoms gonorrhea buy trazodone 100 mg with amex. The structure of the outcomes framework has been chosen to be useful to those involved in planning and designing new undergraduate medical degree programmes treatment nurse buy trazodone on line. The Level 1 outcomes describe domains of teaching, learning and assessment that lend themselves to becoming “curriculum themes”, with defned academic leadership and dedicated resources. The Level outcomes can help to defne the content of such themes in terms of teaching, learning and assessment. The Professionalism outcomes are relevant when addressing the personal and professional development and ftness to practise of medical students. In future work we aim to document best practice in learning, teaching and assessing these outcomes. Meantime useful information on outcome-based assessment can be accessed through the Scottish Doctor website (http://www. Mobility It seems likely that schools which share a common set of graduating learning outcomes will fnd it much more straightforward to exchange students and staf, particularly in the later parts of the curriculum. Similarly, assurance that graduates have achieved the necessary learning outcomes is likely to facilitate mobility of doctors in Europe and provide reassurance to employers and patients. Quality enhancement and quality assurance Consideration of a medical school’s graduating outcomes in relation to an agreed framework should be an integral part of quality assurance and accreditation, sitting alongside evaluation of education process and infrastructure. Recently developed methodologies permit systematic mapping of one outcomes framework against another, so that a school’s learning outcomes could simply be cross-referenced against the European framework (Ellaway, R et al, 007). Although it is likely that national systems of quality assurance and accreditation will continue to predominate in Europe, the Tuning outcomes can support a developing European dimension in medical education as part of a harmonisation process. European Ministers of Education (1999) Joint declaration of the European Ministers of Education convened in Bologna on the 19th of June 1999 [The Bologna Declaration]. Joint Quality Initiative informal group ( 004) Shared ‘Dublin’ descriptors for Short Cycle, First Cycle, Second Cycle & Third Cycle Awards. Ensuring global standards for medical graduates: a pilot study of international standard-setting. Association of American Medical Colleges (1998) Learning objectives for medical student education: Guidelines for medical schools. Medical Teacher, 007; 9:636-641 3 Appendix A: Knowledge Outcomes Although not formally part of Tuning methodology, the web-base questionnaire survey also sought opinion about important areas of knowledge for medical graduates. In general, the highest scores and rankings related to knowledge of traditional scientifc disciplines which underpin medical practice, such as physiology, anatomy, biochemistry, and immunology, together with clinical sciences such as pathology, microbiology and clinical pharmacology. The lowest ranking related to knowledge of “diferent types of complementary / alternative medicine and their use in patient care”. Graduates from medical degree programmes in Europe should be able to demonstrate knowledge of: Basic Sciences Normal function (physiology) Normal structure (anatomy) Normal body metabolism and hormonal function (biochemistry) Normal immune function (immunology) Normal cell biology Normal molecular biology Normal human development (embryology) Behavioural and social sciences Psychology Human development (child/adolescent/adult) Sociology Clinical Sciences Abnormal structure and mechanisms of disease (pathology) Infection (microbiology) Immunity and immunological disease Genetics and inherited disease 4 Drugs and prescribing Use of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance Principles of prescribing Drug side efects Drug interactions Use of blood transfusion and blood products Drug action and pharmacokinetics Individual drugs Diferent types of complementary / alternative medicine and their use in patient care Public Health Disease prevention Lifestyle, diet and nutrition Health promotion Screening for disease and disease surveillance Disability Gender issues relevant to health care Epidemiology Cultural and ethnic infuences on health care Resource allocation and health economics Global health and inequality Ethical and legal principles in medical practice Rights of patients Rights of disabled people Responsibilities in relation to colleagues Role of the doctor in health care systems Laws relevant to medicine Systems of professional regulation Principles of clinical audit Systems for health care delivery 5 Appendix B: Clinical Attachments and Experiential Learning Although not formally part of Tuning methodology, the web-base questionnaire survey also sought opinion about which areas of clinical medical practice were most important to be included as part of the core undergraduate medical school programme. In general, the highest rankings related to acute medical and surgical care settings, with community and primary care also ranking highly. The lowest rankings related to areas of specialised surgical and medical practice. If your curriculum vitae is in a different format but still provides all of the information shown on the model curriculum vitae below, you may submit it with your application. You can modify it to reflect your individual circumstances, eliminating sections that do not pertain to your activities. There should be no gaps since medical school graduation, domestic or international, as this may cause a delay in processing your application. List membership on editorial boards, position as scientific reviewer for medical journal, etc. These activities relate to service in other medical societies or volunteering in free clinics for the indigent, as well as to service in the lay community, such as coaching little league teams or participating on local school boards, etc. In the case of x-rays the source is on the outside of the pa- tient and the detector is on the other side – unless in the case of backscattered x-rays. We also intend to look in more detail into the use of radioactive isotopes for diagnostic purposes. Furthermore, the iso- topes are inside the body – and it is the g-photons coming out that yield the information. Whether the distribution of activity deviates from normal in an organ or part of the body. The electromagnetic radiation is within the radio frequency feld and can not ionize.
Vak, 46 years: In relation to animals fungi do not possess chloroplasts, however similarly to plants fungi maintain a cell wall, vacuoles, and may produce by both sexual and/or asexual means. Artificial media can be used to grow the micro- organism from a dead animal, hides, skin, wool or soil.
Potros, 49 years: Leucine and isoleucine have both been shown to promote bladder carcinogenesis in a two-stage rat model. A severe post-impact fre engulfed the aircraft fuselage, fatally injuring all six occupants.
Goose, 33 years: Dietary fat undergoes lipolysis by lipases in the gastro- intestinal tract prior to absorption. Diagnostic tests are a way of obtaining information that provides a basis for revis- ing disease probabilities.
Leon, 57 years: The following section looks at the factors involved in the different stages of drug use and specifically the different types of drug use som e young people m ay typically experience. Haemoglobin and antiendomysial antibodies ing, diarrhoea, anorexia or abdominal distension at any may be checked at routine follow-up to look for inad- age.
Pakwan, 42 years: The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Effects of familial predisposition to obesity on energy expenditure in multiethnic prepubertal girls.
Thorek, 62 years: The main issue was understanding how a patient’s identity is protected under each model and how access to this data is managed. By tailoring the elements and dosages in the cocktail to the genetic signature of the virus, far more rapid and efficient clearing of the virus has been achieved.
Fadi, 28 years: In other words, dental radiology could be described as a high volume, low dose procedure. Although it is beyond the scope of this report to suggest detailed reforms of the medical-school curriculum, the Committee would like to emphasize that full realization of the power of the Knowledge Network of Disease and the New Taxonomy derived from it would almost certainly require a major shift in educational strategy.
Jorn, 40 years: A sigmoid colectomy and end-to-end of small volume stool, which may relieve discomfort. It is notable that despite the substantial number of published investi- gations in which glutamine has been administered to humans, very few, if any adverse effects have been reported.
Grim, 61 years: The resident should keep detailed colleague and demonstrating support or empathy will assist in records of the reasons for reporting and of discussions easing the tension in these circumstances. Macroscopy The tumour is usually a polypoid mass on a stalk, its sur- Microscopy face covered with thrombus.
Gamal, 21 years: The public health burdens of sedentary living habits: theoretical but realistic estimates. Furthermore, resistance to this drug was recognised early, making research and development of new therapies crucial even for this highly targetable cancer.
Osmund, 23 years: With disease progression, con >2 scores positive, >50% involvement in core sider combined androgen blockade with anti sample). Lowell Levin is a professor at Yale University School of Medicine: 57 "Twelve of the thirteen chapters in this book are devoted exclusively to evidence of misconduct and mayhem perpetrated on an unsuspecting public [by the medical profession].
Mirzo, 31 years: In addition, the stu- dy of genomics can provide information about an individu- 1. For experience, an uphill battle at best, lack the power to provide example, upon learning that a patient with a headache that the intelligence needed to inform learning organizations.
Rakus, 54 years: Crit Care Med 2008; 36:3190–3197 ventilated patients in an adult surgical intensive care unit. These lesions are characteristically associated with lower motor neurone signs at the level of transection and upper motor neurone signs below the level.
Harek, 22 years: This approach has been successfully adopted for many of the infections that were previously common childhood, e. She became certifed as a Family Physician in 1988 and subsequently as a psychiatrist in 1995.
Tangach, 52 years: Comply with recommended soak times and concentrations (risk of corrosion of metal instruments). The investigator concludes that disclosure of the risks may discourage participation in the trial.
9 of 10 - Review by M. Darmok
Votes: 142 votes
Total customer reviews: 142
References
- Kang YS, Kamm MA, Engel AF, et al. Pathology of the rectal wall in solitary rectal ulcer syndrome and complete rectal prolapse. Gut 1996;38:587.
- National Institutes of Health. ClinicalTrials.gov: Surgery in treating patients with early stage anal canal or perianal cancer and HIV infection. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02437851? cond=anal+cancer+hiv&draw=6&rank=26.
- Brown AFT. Critical care. In: Cameron P, Jelinek G, Kelly A, et al, editors. Textbook of adult emergency medicine. 3rd ed. Edinburgh: Elsevier; 2009.
- Daugbjerg P, Brenoe E, Forchhammer H, et al. A comparison between nebulized terbutaline, nebulized corticosteroid and systemic corticosteroid for acute wheezing in children up to 18 months of age. Acta Paediatr 1993; 82: 547-551.
- Al-Khoury G, Kaufman D, Hirshberg A. Improved control of exposed fi stula in the open abdomen. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;206:397-398.