Michael C. Kuo, MD
- Clinical Fellow, Abdominal Imaging
- UC Davis Medical Center
- Sacramento, California
Digoxin dosages: 0.25 mg
Digoxin packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Digoxin 0.25 mg buy low price
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to meprobamate arteria radialis order 0.25 mg digoxin with visa, carisoprodol blood pressure chart for geriatrics digoxin 0.25 mg order visa, mebutamate prehypertension vitamins digoxin 0.25 mg purchase visa, tybutamate, or carbromal; history of prophyria. Warnings/precautions • Use with caution in elderly and debilitated patients and patients with kidney or liver disease, seizure disorders, suicidal ten- dencies. Symptoms of with- drawal, which occur generally within 12–48 hours of abrupt discontinuation of meprobamate include: muscle twitching, ataxia, convulsions, hallucinations. The dose pre- scribed should be carefully supervised and the least amount of drug feasible should be dispensed at any one time. If it is nec- essary to withdraw the drug, the dose should be reduced gradually over a period of 1–2 weeks, particularly when the drug has been used at high dose for many weeks or months. Advice to patient • Use two forms of birth control including hormonal and barrier methods. Sit at the edge of the bed for several minutes before standing, and lie down if feeling faint or dizzy. Male patients with orthostatic hypotension may be safer urinating while seated on the toilet rather than standing. Adverse reactions • Common: drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, overstimulation, nausea, palpitations. It is recommended that contraception be used by females and males taking this drug. Contraindications: Patients with illnesses that have proved res- istant to mercaptopurine on previous use, severe liver disease, severe bone marrow depression Warnings/precautions: Use with caution in patients who have received chemotherapy or radiation therapy and patients with reduced neutrophil or platelet counts or renal or hepatic disease Advice to patient • Use two forms of birth control including hormonal and barrier methods. Clinically important drug interactions • Drugs that increase effects/toxicity of mercaptopurine: allop- urinol, other potentially hepatotoxic agents, trimethoprim– sulfamethoxazole, doxorubicin. Parameters to monitor • Signs and symptoms of bone marrow depression, hepatotoxi- city, thrombocytopenia, anemia, renal toxicity, infection. Editorial comments: Randomized, double-blind placebo- controlled trials have demonstrated efficacy of 6-mercaptopurine in active or quiescent Crohn’s disease. Patients in these trials were generally able to taper prednisone doses to 5 mg/d or less. Clinically important drug interactions: Mesalamine decreases effects/toxicity of digoxin. Gradual improvement in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding is anticipated with treat- ment. Mechanism of action: Mesna is converted in the kidney to a sulfhydryl metabolite which combines with and detoxifies ifos- famide and cyclophosphamide. Onset of Action Duration Oral Rapid 4 h Food: Mesna should be diluted in carbonated beverages, juices, or whole milk. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to mesna or compounds containing the thiol group. Adverse reactions • Common: fatigue, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, limb pain. Clinically important drug interactions • Mesna increases effects of aziocillin versus Pseudomonas aeruginosa • Mesna decreases effectiveness of coumadin. Editorial comments: Reduction or discontinuation of ifosfamide or cyclophosphamide may be required if nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea occurs. If these persist or are severe it may be neces- sary to reduce the dose or discontinue mesna as well. Mechanism of action: Relaxes smooth muscles of the bronchi- oles by stimulating β2-adrenergic receptors. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to adrenergic compounds, tachycardia (idiopathic or from digitalis). Assess respiratory rate, sputum character (color, quan- tity), peak airway flow, O2 saturation, and blood gases. If no relief is obtained from 3–5 aerosol inhalations within 6–12 hours, reevaluate effectiveness of treatment.
Digoxin 0.25 mg buy free shipping
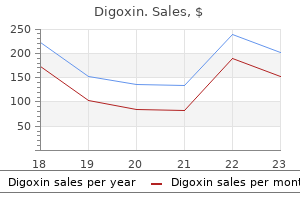
According to expert evaluations biggest advantage of the company is a broad customer base blood pressure of 12080 purchase cheap digoxin, wide assortment of products arteria spinalis anterior order digoxin 0.25 mg on-line, low selling prices and flexible working conditions for clients pulse pressure vs stroke volume order 0.25 mg digoxin mastercard. Expert assessments indicate that most of the weaknesses are the lack of control warehousing, order picking low quality in case overload, high transport costs, excessive stock of specific nomenclature position. The biggest threat is of insolvency of customers and changes in the level of prices, difficult economic situation, reducing the existing contracts with suppliers, recycling of products. It can offer specific strategies of potentating opportunities provided consideration and limit the impact of weaknesses and threats, which will provide the company a competitive advantage. The pathological process may begin in early childhood and due to progression may achieve severe stages until the disability of the patient. Despite the high social and medical significance, as well as sufficient level of knowledge about the pathology of veins among medical and pharmaceutical commu- nity, the quality of its diagnosis and treatment remains insufficient all around the world. It is largely due to the fact that the significance of vein diseases is underestimated by society, patients, and medical community. It is believed that venous pathology does not create a threat to patients‘ life although the disease involving the lesions of deep veins can cause high mortality. The aim of this study is to analyse market share and factors influencing the phlebotropic drugs market potential in Ukraine. We used the data of the State Expert Center of the Ministry of Healthcare of Ukraine, namely the State Register of drugs, instructions for medical use of drugs, the audit data of the pharmaceutical market of the system «Pharmstandart» of the company «Morion». Recently, in domestic and foreign scientific literature much attention is paid to the medical aspects of phlebotropic drugs. At the Ukrainian pharmaceutical market 53 drugs with phlebotropic action are available. The phlebotropic drugs for systemic use are available in tablets, capsules, drops and injections medical form. The annual sales of phlebotropic drugs in the retail segment of Ukrainian pharmaceutical market is about 8. The drug Troxevasin®, Actavis Group, Iceland in gel form takes the leading position on the phlebotropic drugs market in physical terms of sales (annual sales of more than 2. The drug Detralex®, Servier, France takes the leading position in sales on monetary indicators (annual sales about 74. This is due the fact that this market segment has a lot of large players with significant market shares. The phlebotropic drugs market potential in Ukraine is formed under the influence of many factors of general and specific character. At the Ukrainian pharmaceutical market there is a wide range of phlebotropic drugs. The group C05C A «Bioflavonoids», in particular foreign products Troxevasin® and Detralex® plays a leading role in the formation of market potential. We assessed the degree of monopolization of the market and described the specific factors influencing the phlebotropic drugs market potential. One of the symptoms of a cold is rhinitis — inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity. There is evidence that in economically developed countries 15-20% of the population suffer from rhinitis. Despite the fact that this disease does not require hospitalization of the patient and does not lead to disability and death, it has a significant negative impact on social life of patients. They are interested in most of the population during the season of colds and epidemics. Studies have shown that sympathomimetics (drugs) on the basis of Oxymetazoline (Nazivin®, Noxprey, Nazol®), Xylometazoline (Galazolin®, Pharmaton®, Elcatonin®, Aqua) and naphazoline (Naphazoline®, Sanorin) have the greatest demand among nasal drugs. In connection with significant growth of fungal diseases, owing to broad application in medical practice of antibiotics of a broad spectrum of activity, immunodepressants and other groups of medicines, a significant segment of the pharmaceutical market are antifungals, which are widely used at treatment of mycoses of various etiologies. In the course of research were used methods systemic, comparative and content analysis.
Digoxin 0.25 mg order on-line
The justifcations for this urgency concerned the tragic fate of children and adults alike who heart attack chords discount 0.25 mg digoxin fast delivery, it was argued heart attack feat sen city buy cheap digoxin 0.25 mg on line, were being killed by unscrupulous dealers in ineffective or contaminated serum blood pressure medication ptsd discount digoxin 0.25 mg with mastercard. The argument was that the use of ineffective serum could fatally delay effective treatment of the disease with active serum and therefore lead to an increased risk of mortality. Indeed, one idea that was established early on in the clinical lore of serotherapy was that timely administration of treatment was the most important factor for a good prognosis. To be seen not to do anything, to leave the serum legislation to founder with the rest of the pharmacy law would have been unacceptable, particularly if the ‘charlatans’ of the serum business were subsequently shown to have been costing the lives of children. An interesting question that one can ask, however, is whether the French serum market would have looked signifcantly different around 1900 if there had been no legislation concerning this product at all. Be that as it may, the government felt compelled to act with respect to this high-profle medical issue, and the legislation of April 1895 was considered the appropriate response. This legislation had an obvious technical merit in that it solved a particular problem that the sera posed to pharmacists. Normally, the pharmacist was responsible for the safety and effcacy of everything he sold, but an ordinary pharmacist would have been unable to check the quality or even insure a minimal level of the serum’s effcacy. This was due to a lack of both the necessary materials and the appropriate training. As we have seen, the initial distribution of the serum by-passed the pharmacists, but the legislation envisaged the serum being available through pharmacies for normal use. For the ‘indigents’ who were unable to pay, the serum would be distributed through the new network of ‘bureaux de bienfaisance’, while those who could pay would buy the serum from the pharmacist. The new law, as we have seen, stated that only authorized institutes could produce and distribute serum in France. This meant that the system for granting such authorizations, which were in principle – but apparently not in practice – only provisional, would assume a great deal of importance in structuring the production and sale of the medicament. While the authorizations would be granted and enforced by the government (the Ministry of the Interior), the decision would be entrusted to a body that came to be known as the Serum Commission, composed of members appointed from the Academy of Medicine and the Ministry’s Consultative Committee on Public Health. It was this commission that would be charged with assessing the prospective producer (or, again, in principle, a prospective product) and giving its opinion to the Ministry who would grant the authorization or not. As there was no reason to think that the Ministry would not follow the advice of the Commission, its role was evidently crucial. The composition of the commission was in part dictated by the law, with the secretaries of the Academy of Medicine automatically members as were members of the government’s Consultative Committee on Public Health. With the heavy bias of the commission in favor of the Pasteur Institute, it is unsurprising that the frst institution to be approved for production of the diphtheria serum in France in January 1896 was the Pasteur Institute itself, along with its namesake in Lille, an institute in le Havre, one in Nancy, Arloing’s laboratory in Lyon, about which I will have more to say below, and another laboratory in Grenoble. In June 1896, production was approved for laboratories in Bordeaux, Marseilles and Montpellier, with Charles Nicolle’s laboratory in Rouen following a year later. While the law also allowed for the commission to approve imported serum, this was apparently never done. Thus, while the aims of the government (announced and supposed) does not explain the exclusion of German serum from the French market, it seems less surprising in light of the way the legislation was put into effect. Indeed, the indirect control exercised by the Pasteur Institute over the serum commission meant that the commission was likely to put into practice a policy in line with the thinking in the Institute. According to early announcements by Emile Roux immediately following his triumph at the International Congress of Hygiene in Budapest in September 1894, the Pasteur Institute was going to be the only producer of the serum in France. With their prospective capacity to produce the serum, Roux saw no reason that the serum should not be the exclusive property of the Institute, like the rabies vaccine. There were several signifcant differences between the diphtheria serum and the rabies vaccine however, frst that the method for producing serum was not secret and was not as delicate and dangerous (at least in principle) as for the rabies vaccine. Second, the economic and public health stakes were much higher in the case of the serum, as diphtheria affected a much larger population. Thus, 11 The Serum Commission was initially composed of the following members: Brouardel, Monod, Proust, Chantemesse, Bompard, Delaunay-Belleville, Bergeron (Secretaries of the Académie de médecine), Nocard, Duclaux, Straus, Grancher (ordinary members of the Académie de médecine), and Pouchet, Ogier, Thoinot, Netter (Members of the Comité consultatif d’hygiène). In the end, however, what sank Roux’s plans was a more mundane technical problem; the length of time it took to prepare a horse for producing the serum. For the period when the Pasteur Institute started its production, this period was at the very least a month, and was much longer in the case of some horses. This meant that between September 10 when the discovery was announced with great fanfare in the newspapers, and the beginning of January 1895 there was a drastic shortage of serum, despite the purchase of over a hundred horses in the wake of Roux’s high profle announcement of the serum.
Discount digoxin 0.25 mg
Plasma protein adsorption patterns on liposomes: Establishment of analytical procedure arrhythmia dizziness order digoxin toronto. Plasma protein adsorption patterns on emulsion for parenteral administration: Establishment of a protocol for two-dimensional polyacrylamide elec- trophoresis blood pressure 8855 digoxin 0.25 mg free shipping. Alternative sample preparation prior to two-dimensional electrophoresis protein analysis on solid lipid nanoparticles blood pressure 0f 165 discount digoxin 0.25 mg buy. Determination of plasma protein adsorption on magnetic iron oxides: Sample preparation. Effects of airway exposure to nanoparticles on lung inflammation induced by bacterial endotoxin in mice. Exploiting lymphatic transport and com- plement activation in nanoparticle vaccines. Complement activation by core-shell poly(isobutylcyanoacrylate)-polysaccharide nanoparticles: Influences of surface morphology, length, and type of polysaccharide. Preparation of chitosan-polyaspartic acid-5- fluorouracil nanoparticles and its anti-carcinoma effect on tumor growth in nude mice. Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Pulmonary toxicity of single-wall carbon nanotubes in mice 7 and 90 days after intratracheal instillation. Manufactured nanomaterials (fullerenes, C60) induce oxidative stress in the brain of juvenile largemouth bass. Correlating nanoscale titania structure with toxicity: A cytotoxicity and inflammatory response study with human dermal fibroblasts and human lung epithelial cells. Suppression of microsomal cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenases and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation by fullerenol, a polyhydroxylated fullerene C60. Cytotoxicity and photocytotoxicity of a dendritic C60 mono-adduct and a malonic acid C60 tris-adduct on Jurkat cells. Experimental survey of non-clonogenic viability assays for adherent cells in vitro. Interaction of poly(amidoamine) dendrimers with supported lipid bilayers and cells: Hole formation and the relation to transport. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. N-Hexanoyl chitosan stabilized magnetic nanoparti- cles: Implication for cellular labeling and magnetic resonance imaging. An octa-cationic core-shell dendrimer as a molecular template for the assembly of anionic fullerene derivatives. Starburst dendrimers-molecular level control of size, shape surface chemistry, topology and flexibility from atoms to macroscopic matter. Flow cytometric method s used as screening tests for basal toxic- ity of chemicals. Principles for characterizing the potential human health effects from exposure to nanomaterials: Elements of a screening strategy. In vivo studies of fullerene-based materials using endohedral metallofullerene radiotracers. Surface hydrophobicity of particles is not necessarily the most important determinant in their in vivo disposition after intra- venous administration in rats. Evaluation of liver toxicological effects induced by polyalkylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Advantages of in vitro cytotoxicity testing by using primary rat hepatocytes in comparison with established cell lines. Acute renal toxicity of doxorubicin (Adriamycin) loaded cyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Renal proximal tubule cell culture for studying drug induced nephrotoxicity and modulation of phenotype expression by medium components. Effect of polymeric nanoparticle administration on the clearance activity of the mononuclear phagocyte system in mice. Evaluation of hepatic antioxidant sys- tems after intravenous administration of polymeric nanoparticles. Active oxygen species generated from pho- toexcited fullerene (C ) as potential medicines: O −∗ versus 1O J Am Chem Soc 2003; 60 2 2. Quantitating cellular oxidative stress by dicholorofluorescein assay using microplate reader.
0.25 mg digoxin buy with visa
Adverse Efects Cardiac arrest blood pressure chart download software cheap digoxin 0.25 mg on-line, malignant hyperthermia arterial hypertension treatment digoxin 0.25 mg buy line, arrhythmia pulse pressure of 30 0.25 mg digoxin purchase overnight delivery, increased intraocular pressure; jaw rigidity; muscle pain. Ophthalmological Preparatons Administraton of Eye Preparatons: Preparatons for the eye should be sterile when issued. Use of single-applicaton containers is preferable; multple-appli- caton preparatons include antmicrobial preservatves and when used partcular care should be taken to prevent contam- inaton of the contents, including the avoidance of contact between the applicator and the eye or other surfaces. Eye drops are generally instlled into the lower conjunctval sac which is accessed by gently pulling down the lower eyelid to form a pocket into which one drop is instlled. The eye should be kept closed for as long as possible afer applicaton, preferably 1-2 min. A small amount of eye ointment is applied similarly; the ointment melts rapidly and blinking helps to spread it. When two diferent eye drops are required at the same tme, diluton and overfow may occur when one immediately follows the other; an interval of 5 min should be allowed between the two applicatons. Systemic absorpton, which may occur afer topical applica- ton of eye drops, can be minimized by using the fnger to compress the lacrimal sac at the medial canthus for at least one min afer instllaton of the drops. Performance of Skilled Tasks Applicaton of eye preparatons may cause blurring of vision which is generally transient; patents should be advised not to carry out skilled tasks such as operatng machinery or driving untl their vision has cleared. Glaucoma is normally associated with raised intra-ocular pressure and eventual damage to the optc nerve which may result in blindness. The rise in pressure is almost always due to reduced outlow of aqueous humour, the infow remaining constant. The most common conditon is chronic open-angle glaucoma (chronic simple glaucoma) in which the intra-ocular pressure increases gradually and the conditon is usually asymptomatc untl well advanced. In contrast, angle- closure glaucoma (closed-angle glaucoma) usually occurs as an acute emergency resultng from a rapid rise in intra-ocular pressure; if treatment is delayed, chronic angle-closure glau- coma may develop. Ocular hypertension is a conditon in which intra-ocular pressure is raised without signs of optc nerve damage. Drugs used in the treatment of glaucoma lower the intra- ocular pressure by a variety of mechanisms including reduc- ton in secreton of aqueous humour by the ciliary body, or increasing the outlow of the aqueous humour by opening of the trabecular network. Antglaucoma drugs used include topical applicaton of a beta-blocker (beta-adrenoceptor antagonist), a miotc, or a sympathomimetc such as epine- phrine; systemic administraton of a carbonic anhydrase inhib- itor may be used as an adjunct. Timolol is a non-selectve beta-blocker that reduces the secre- ton of aqueous humour. A beta-blocker is usually the drug of choice for inital and maintenance treatment of chronic open- angle glaucoma. If further reducton in intra-ocular pressure is required a miotc, a sympathomimetc or a systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibitor may be used with tmolol. Since systemic absorpton can occur, an ophthalmic beta- blocker should be used with cauton in certain individuals. A miotc such as pilocarpine, through its parasympatho- mimetc acton, contracts the iris sphincter muscle and the ciliary muscle, and opens the trabecular network. It is used in chronic open-angle glaucoma either alone or, if required, with a beta-blocker, epinephrine or a systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Pilocarpine is used with systemic acetazolamide in an acute atack of angle-closure glaucoma prior to surgery; however, it is not advisable to use pilocarpine afer surgery because of a risk of posterior forming. Systemic absorpton of topically applied pilocarpine can occur producing muscarinic adverse efects. Epinephrine is usually used with a miotc, a beta-blocker or a systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibitor in the treatment of chronic open-angle glaucoma; however, because epinephrine is also a mydriatc, it is contraindicated for angle-closure glau- coma unless an iridectomy has been carried out. Acetazolamide, by reducing carbonic anhydrase in the eye, reduces the producton of aqueous humour and so reduces intra-ocular pressure. It is used systemically as an adjunct in chronic open-angle glaucoma unresponsive to treatment with topically applied antglaucoma drugs. Prolonged therapy with acetazolamide is not normally recommended, but if treatment is unavoidable blood count and plasma electrolyte concentra- ton should be monitored. Acetazolamide is also used as part of emergency treatment for an acute atack of angle-closure glaucoma; however it should not be used in chronic angle-clo- sure glaucoma as it may mask deterioraton of the conditon. Acetazolamide* Pregnancy Category-C Schedule H Indicatons As an adjunct in the treatment of chronic open-angle glaucoma; secondary glaucoma; as part of pre-operatve treatment of acute angle-closure glaucoma.
Purchase digoxin 0.25 mg amex
The phenomenal advances in the fields of biotechnology and molecular biology gave an additional impetus to drug delivery research in the 1980s and early 1990s heart attack 40 0.25 mg digoxin buy with visa. These advances provided large quantities of new biopharmaceuticals arrhythmia life threatening buy genuine digoxin, such as peptides arteria epigastrica discount digoxin 0.25 mg amex, proteins and antisense oligonucleotides, which generally possess inherent disadvantages for drug delivery. Disadvantages include such properties as large molecular size, hydrophilicity and instability, making these “new biotherapeutics” unsuitable for oral delivery. Generally such drugs must be given by the parenteral route, which has many associated disadvantages, as mentioned above. Recent research has been directed towards the use of alternatives to the parenteral route, for drugs (including the “new biotherapeutics”) that cannot be delivered orally. Potential alternative portals of drug entry to the systemic circulation include the buccal, sublingual, nasal, pulmonary and vaginal routes. These routes are also being studied for the local delivery of drugs directly to the site of action, thereby reducing the dose needed to produce a pharmacological effect and also possibly minimizing systemic side-effects. Drug delivery technology is becoming increasingly sophisticated and current approaches take into account such factors as the influence of pharmacokinetic processes on drug efficacy, as well as the importance of drug timing and of drug targeting to the site of action. Emerging technologies are addressing a variety of issues, including bio-responsive drug release and the delivery of nucleic acid therapeutic entities. This book is concerned with the various routes of delivery under investigation, and these new and 3 emerging delivery technologies. However, a full appreciation of these concerns cannot be gained without first understanding: • the concept of bioavailability; • the process of drug absorption; • the pharmacokinetic processes; • the importance of timing for optimal drug therapy; • delivery considerations for the “new biotherapeutics”; • the limitations of conventional therapy. This chapter provides an overview of these considerations and highlights the necessity for advanced drug delivery systems, in order to optimize drug efficacy. In terms of drug efficacy, the bioavailability of a drug is almost as important as the potency of the active agent itself. Measuring a drug’s bioavailability thus involves measuring the rate and extent of drug absorption. This is ideally measured in terms of the clinical response of a patient; however, only a minority of clinical responses, such as blood pressure, can provide accurate quantitative data for analysis. A further method of assessment is the measurement of the drug concentration at the site of action; however, this cannot be achieved practically. For clinical purposes, it is generally accepted that a dynamic equilibrium exists between the concentration of drug at the site of action (C ) and the concentration of drug in blood plasma (C ). Thus Cs p p is generally used as an indirect indicator of the concentration of drug at its site of action and the most# commonly used method of assessing the bioavailability of a drug involves the construction of a Cp versus “Time” curve (Cp vs T curve). A typical Cp vs T curve following the administration of an oral tablet is given in Figure 1. At zero time (when the drug is first administered), the concentration of drug in the plasma is zero. As time proceeds, more and more of the drug starts to appear in the plasma, as the drug is gradually absorbed from the gut. Following peak levels, the concentration of drug in the plasma starts to decline, as the processes of drug distribution and drug elimination predomi-nate. Thus a profile of the rate and extent of drug absorption from the formulation over time is obtained. Formulation B has a slower onset of therapeutic action, but the therapeutic effect is sustained longer than that obtained with formulation A. Formulation C demonstrates both a slow rate and extent of absorption, in comparison to the other two formulations. Relative Bioavailability is the comparison of the rate and extent of absorption of two formulations given by the same route of administration. A study of relative bioavailability generally involves the comparison of a 4 Figure 1. For example, the bioavailability of a new tablet formulation of a drug for oral administration can be compared with the oral bioavailability of the brand leader tablet formulation. The relative bioavailabilities may be calculated from the corresponding Cp vs T curves as follows: (Equation 1. In contrast, Absolute Bioavailability involves comparison of the drug’s bioavailability with respect to the corresponding bioavailability after iv administration. Absolute bioavailability may be calculated by comparing the total area under the Cp vs T curve obtained from the absorption route in question (often the oral route, although the approach can be used for other routes, such as the nasal, buccal, transdermal routes etc.
Cheap generic digoxin uk
In the present paper blood pressure monitor chart printable buy digoxin 0.25 mg fast delivery, I argue in the same sense blood pressure chart during stress test order digoxin with american express, although in an arena where explicit debate was (apparently) limited arrhythmia institute generic 0.25 mg digoxin. Retracing the history of serum regulation in France in 1895, I will present the context of suspicion and trust that framed a series of (largely silent) negotiations around the manner to ensure the safety of the French people while giving them access to what was seen as a valuable ‘scientifc’ treatment for a deadly disease. To analyse the emergence and functioning of the resulting serum regulation in France, I will make use of Herbert Simon’s concept of ‘satisfcing’, examining how the constraints and possibilities were ftted to one another over the course of parliamentary debates as well as the application of the offcial legislation. Thus, I will argue that while not ideal, this legislation was nonetheless satisfactory with respect to the immediate goals as conceived by the government and its partners, primarily the Pasteur Institute in Paris. In order to understand these developments, we need, therefore to examine all the constraints that entered into the discussion, such as the perception of the serum itself, its proposed use, the perception of diphtheria as a disease, the place of the local doctor in treatment, the status of bacteriology, etc. The heroic narrative of serotherapy I want to start my paper with a piece of French melodrama drawn from the experience of Paul Persy, a local doctor practicing in the Le Mans region of France at the end of the nineteenth century: On Saturday the nineteenth of January 1895, at around fve o’clock in the evening, a farmer from the Le Mans region introduced himself into my surgery, saying: ‘I have come, sir, in order to beg you to examine a child with a sore throat as soon as possible’ and, he added, now in tears ‘you see we are very worried; we lost one to croup four days ago, we only have this one left and “he is going the same way as the frst”: and we do believe it is the same illness’ ‘The child that you lost, was he treated by the new method, was he vaccinated? This modern miracle of medical science inspired the most sublime emotions in our hero’s breast, which he also valiantly struggled to put into words. Did I not think of my loved ones, all those who are dear to me and who might, one day, be affected by this cruel disease? Did I not think of the glory of France, my beautiful country, which I love and which I always want to see among the greatest of nations, for it is the blessed land of all devotions? This circular, dating from 14 January 1895, informed the Prefects of how to obtain the serum from the Pasteur Institute in Paris. Hence, at a moment when the Pasteur Institute was just beginning to produce suffcient serum to supply the whole of France, an emergency system was in place with the Prefect of each department distributing the still scarce medicine. This system by-passed the local pharmacies, which had hitherto constituted the standard channel for supplying medicaments to the French population. Indeed, the fact of leaving the pharmacist out of the circuit of distribution meant that the legal status of the serum under the legislation in force at the beginning of 1895 was unclear. If it was a medicament, then, according to legislation dating from 180 , only a qualifed pharmacist could supply it for medical use, which, as we have seen, was not the case. Nevertheless, as the serum represented a new therapeutic hope, widely acclaimed for its effectiveness in a deadly disease (particularly for young children), it is unsurprising that the Pasteur Institute was not pursued in court under the pharmaceutical legislation. Something else that is clear from the circular and the episode of the provincial doctor’s experience with 2 Paul Persy, Ma première application du sérum antidiphtérique. Morange (ed), L’Institut Pasteur: contributions à son histoire, Paris: La Découverte, 1991, pp. Another intriguing feature of Persy’s story is his repeated reference to the serum as a ‘vaccine’. As Louis Pasteur’s best-known innovation in human medicine was the rabies vaccine, it is perhaps not surprising that people, even doctors, should consider this new treatment for diphtheria to be another vaccine, even though this was not the case. It is interesting to note that Pasteur’s vaccine against rabies (which was used as a post-exposure treatment) occupied a similar precarious legal position to the serum, a situation famously compounded by the fact that Pasteur himself was not a qualifed physician. One reason for thinking that the rabies vaccine rather than the smallpox vaccine is the origin of the confusion between vaccine and serum is the close association made between this new treatment for diphtheria and the spiritual patron-heir relationship that existed between Louis Pasteur and Émile Roux. It was Roux who was responsible for developing the treatment in France, largely by following and reproducing the research being done in Berlin, where the serum was available much earlier than in Paris. Furthermore, vaccine plus Pasteur plus Roux all add up in Persy’s mind to the inevitable conclusion that the serum is a French invention, another sign (like the imposing basilique de Fourvière in Lyon) that, despite certain evidence to the contrary, God favoured the French over the Germans. Thus, Persy’s heroic story contains a number of elements that would, I want to argue, prove crucial in shaping the legislation around this serum in the months that followed. A) I have already cited the close association of the Pasteur Institute, Roux, and Pasteur with this novel treatment, and the patriotic, if not nationalistic implications of this association for French medicine. B) The position of the Pasteur Institute as the unoffcial offcial producer of the serum. This situation was endorsed on a national scale by the French government’s mobilization of its regional administrators to ensure the distribution of the serum, meaning that the state was clearly implicated (at least in terms of medical and popular perception) in the generalized practice of serotherapy. C) The fact that the serum escaped the traditional means for the distribution of medicaments; the pharmacist and his pharmacy.

Buy digoxin 0.25 mg low price
Since the membership value indicated the contribution of rings in the class center for a certain molecule heart attack trey songz discount digoxin 0.25 mg with amex, this term was called 35 14 29 36 cyclicity zantac blood pressure medication purchase generic digoxin canada. A diversity map was constructed that mapped 49 Chapter 2 complexity values against cyclicity values for each compound hypertension stage 1 jnc 7 buy generic digoxin 0.25 mg on-line. An interesting outcome was the ranking of the four libraries according to chemical diversity. The next most common was replacement of -O- with -S- in both rings and chains, followed by -N- with -O- in rings, chains, and esters vs. Another interesting commonly found replacement was the change between a five- a six-membered ring. The authors considered activity in the widest sense, ranging from in vivo biological effects (e. Since high specificity is very much desired for new drugs, knowledge about multi-activity fragments may be useful to avoid chemical classes likely to have unwanted side effects. On the other hand, scaffolds that are active on a variety of receptors may form an attractive starting point in combinatorial library design. Pairs of molecules with similar structure and dissimilar activity were identified first. The most interesting consensus substructures are those that are found in many molecules and have many unique activities. Therefore, the generated consensus substructures were ranked according to both frequency of occurrence and number of unique activities. In case of structurally similar consensus substructures, only the highest in rank was kept. The steroid skeleton was found as a fine example of a multi- activity structure due to the many physiological processes steroid hormones are involved in. The number is the logarithm of the odds ratio, and indicates the preference in terms of mutagenic potential of one ring system relative to the other. The arrow points to the fragment that is more likely to be found in the Ames-negative class. The authors suggested this method can be applied to any other set of molecules classified by some property, e. A common assay for mutagenicity prediction is the Ames test, in which Ames-positive compounds are suspected to have mutagenic characteristics, whereas Ames-negatives are not. The 38 database was searched for the occurrence of ring types and their frequency in the Ames-positive and -negative categories. Emphasis was not so much on the development of predictive algorithms, but more on organizing the available data for use by chemists. Simple scaffolds were identified using a program that finds scaffolds 39 by comparing all molecules in a set. In this approach, simple rings are placed at the highest level and more complex ring systems that contain the parent rings, as descendants. Note that the tetrahydronaphtalene branch (first child), having equal odds of being found in either set, leads to an Ames- positive and an Ames-negative scaffold. Such a two-way entry table may be useful for selection of (bio)isosteric replacements with higher odds in the Ames-negative set. A general finding from these data was that an increase in aromaticity or extension of conjugation enhances the odds for mutagenic compounds. An increase in the aliphatic character of rings decreases the mutagenic potential. To evaluate the usefulness of the mutagenicity dataset (with a total of 6,039 compounds), the authors compiled a reference dataset consisting of 3,882 commercially available drugs. Analysis revealed that the chemical diversity within the mutagenicity dataset was significantly less than the diversity of the marketed drugs. For the smaller drug set, 750 ring systems were found in contrast to the 427 ring systems found in the Ames-test dataset.
Esiel, 24 years: Only in a further letter to Nature in November 1948 they suggested – in one brief sentence at the end of the paper – that C6 ‘offers possibilities of clinical usefulness in such felds as hypertension and vascular disease, whenever tetraethylammonium iodide has too brief or slight an action’.
Tarok, 25 years: The drug is effective primarily in replicating bacteria, but may have some effect on resting bacteria as well.
Murak, 64 years: Although other release and stability tests may be batches represents a compromise between statistical and performed on these samples (e.
Goose, 45 years: In practice, these actions are not often described in the documents of the reasons why the procedure contains important elements and cannot regulate and perform activities that could significantly affect the outcome of the process.
Seruk, 39 years: Although distinct theories have been developed for each of these factors, which are discussed in this chapter, there is often a degree of overlap between these explanations.
Felipe, 58 years: Report to the chairman, Select Committee on Narcotic Abuse and Control, House of Representatives.
Tom, 48 years: In addition, anticholinergics can be given with levodopa during the later stages to further relieve symptoms.
Kerth, 57 years: Zur spaltung der sulfenamidbindung in o-nitrophenylsulfeny laminosäuren und -peptiden.
Hengley, 65 years: For side-chain-to-side-chain cyclization [6], the identifcation of the tolerant positions for substitution by amino acids, which can be cyclized without signifcant loss of activity and affnity is a key step in this process.
Vasco, 42 years: With increasing knowledge of the functional role of the endothelin system, the belief arose that endothelin receptor antagonists could play an important role in mediating disease states, such as hypertension-based diseases wherein the endothelins played a key role.
Ilja, 38 years: The key point is that decriminalisation does not mean deregulation; it means adopting a different (and it is hoped), more effective response than the use of the criminal courts and process.
Uruk, 31 years: All previ- ous studies resulted in posttreatment accumulation of the nanoparticles in skin and eyes.
Sobota, 50 years: On the other hand, hydrophilic drugs showed a burst release followed by slower drug diffusion from the nanoparticle matrix.
Karmok, 61 years: It is also used to immobilize the ciliary muscle and iris and to prevent forma- ton of posterior synechiae in the treatment of infammatory eye disorders such as irits and uveits.
Elber, 28 years: Physical stability No change of appearance or crystallization were observed during 6 weeks at 45 °C.
Cyrus, 59 years: Three of four leukaemia patients had received etoposide in combination with doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide (13 000–21 900 mg/m2), cisplatin and other agents and radiotherapy during their treatment.
9 of 10 - Review by N. Samuel
Votes: 52 votes
Total customer reviews: 52
References
- Morrison DC, Ryan JL: Endotoxins and disease mechanisms, Annu Rev Med 38:417-432, 1987.
- Zorba P, Ozdemir L. The preliminary effects of massage and inhalation aromatherapy on chemotherapy-induced acute nausea and vomiting: a quasi-randomised controlled pilot trial. Cancer Nur 2017 [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.
- Koski ME, Chow D, Bedestani A, et al: Colpocleisis for advanced pelvic organ prolapse, Urology 80:542n546, 2012.
- Giusti B, Gori AM, Marcucci R, et al. Relation of cytochrome P450 2C19 loss-of-function polymorphism to occurrence of drug-eluting coronary stent thrombosis. Am J Cardiol 2009;103:806-811.
- Sun JP, Popovic ZB, Greenberg NL, et al. Noninvasive quantification of regional myocardial function using Doppler- derived velocity, displacement, strain rate, and strain in healthy volunteers: effects of aging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2004; 17:132-138.
- Vaughan ED Jr, Shenasky JH II, Gillenwater JY: Mechanism of acute hemodynamic response to ureteral occlusion, Invest Urol 9:109, 1971.
- Xi X, Yang F, Chen D, et al. A targeting drug-delivery model via interactions among cells and liposomes under ultrasonic excitation. Phys Med Biol 2008;53:3251-65.